Kinetics of plasmatic cytokines and cystatin C during and after hemodialysis in septic shock-related acute renal failure
- PMID: 20546598
- PMCID: PMC2911761
- DOI: 10.1186/cc9064
Kinetics of plasmatic cytokines and cystatin C during and after hemodialysis in septic shock-related acute renal failure
Abstract
Introduction: Cystatin C could be a relevant residual glomerular filtration rate marker during hemodialysis (HD), and a high cytokine plasma (p) rate is associated with an increase in mortality during sepsis. To the best of our knowledge, cytokines and cystatin C kinetics during and after HD during sepsis have never been studied. In this study, we described p cytokines and cystatin C variations during and after hemodialysis in septic-shock patients with acute kidney injury (AKI).
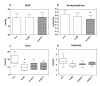
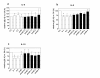
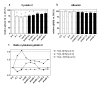
Methods: Ten patients, from two tertiary ICUs, with septic shock-related AKI, according to RIFLE class F, were studied. In this prospective observational study, blood samples were collected at the start, after 1 hour, 2 hours, and at the end of HD with a polymethymethacrylate (PMMA) hemodialyzer (D0, D1, D2, and endD), and 30, 60, 90, 120, and 180 min after HD (postD0.5, postD1, postD1.5, postD2, and postD3). We measured p interleukins (IL)-6, IL-8, IL-10, cystatin C, and albumin. Results are expressed as variations from D0 (mean +/- SD).
Results: During HD, p[IL-6] did not vary significantly, whereas p[IL-8] and p[IL-10] reductions by D1 were 31.8 +/- 21.2% and 36.3 +/- 26%, respectively (P < 0.05 as compared with D0). At postD3, p[IL-8] and p[IL-10] returned to their initial values. p[Cystatin C] was significantly reduced from D1 to postD1, with a maximal reduction of 30 +/- 6.7% on D2 (P < 0.05). Norepinephrine infusion rate decreased from D0 to postD3 (0.65 +/- 0.39 to 0.49 +/- 0.37 microg/kg/min; P < 0.05).
Conclusions: HD allows a transient and selective decrease in p cytokines, which are known as being correlated with mortality during septic shock. Because of a significant decrease in p cystatin C during HD, this should not be considered as an accurate marker for residual glomerular filtration rate during septic acute renal failure when receiving HD with a PMMA hemodialyzer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Plasma Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) predicts acute kidney injury in septic shock at ICU admission].Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2013 Mar;32(3):157-64. doi: 10.1016/j.annfar.2012.11.012. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2013. PMID: 23453486 Clinical Trial. French.
-
C-terminal agrin fragment (CAF) reflects renal function in patients suffering from severe sepsis or septic shock.Clin Lab. 2015;61(1-2):69-76. doi: 10.7754/clin.lab.2014.140724. Clin Lab. 2015. PMID: 25807640 Clinical Trial.
-
Is serum cystatin C a better marker of kidney function than serum creatinine in septic newborns?Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2012 Apr 2;66:175-80. doi: 10.5604/17322693.988679. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2012. PMID: 22470193
-
[Extracorporeal therapy in sepsis].G Ital Nefrol. 2019 Apr;36(2):2019-vol2. G Ital Nefrol. 2019. PMID: 30983171 Review. Italian.
-
Biomarkers of kidney injury.Biomarkers. 2011 Jul;16 Suppl 1:S22-30. doi: 10.3109/1354750X.2011.587129. Biomarkers. 2011. PMID: 21707441 Review.
Cited by
-
An adsorbent monolith device to augment the removal of uraemic toxins during haemodialysis.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014 Jun;25(6):1589-97. doi: 10.1007/s10856-014-5173-9. Epub 2014 Feb 27. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014. PMID: 24573455 Free PMC article.
-
Removal and rebound kinetics of cystatin C in high-flux hemodialysis and hemodiafiltration.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 Jul;9(7):1240-7. doi: 10.2215/CJN.07510713. Epub 2014 May 1. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24789553 Free PMC article.
-
Renal arterial resistive index versus novel biomarkers for the early prediction of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury.Intern Emerg Med. 2024 Jun;19(4):971-981. doi: 10.1007/s11739-024-03558-y. Epub 2024 Mar 6. Intern Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 38446371 Free PMC article.
-
A novel conditional platelet depletion mouse model reveals the importance of platelets in protection against Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia.J Thromb Haemost. 2015 Feb;13(2):303-13. doi: 10.1111/jth.12795. Epub 2014 Dec 30. J Thromb Haemost. 2015. PMID: 25418277 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, cystatin C, and soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 in critically ill patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury.Crit Care. 2015 May 6;19(1):223. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0941-6. Crit Care. 2015. PMID: 25944130 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

