Structural basis for conservation in the CYP51 family
- PMID: 20547249
- PMCID: PMC2962772
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.06.006
Structural basis for conservation in the CYP51 family
Abstract
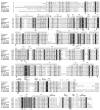
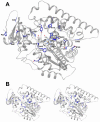
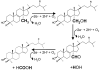
Sterol 14α-demethylases (14DM) comprise the CYP51 cytochrome P450 genome family. The 14DM reaction is essential for the biosynthesis of sterols which are necessary for production of cellular membranes. This is the most widely distributed P450, being present in all biological kingdoms. From one kingdom to another the primary amino acid sequence identity usually ranges between 30 and 20%. In this minireview we describe the conservation of specific amino acids and the various CYP51 orthologs and indicate the roles that they may play in the structure/function of this monooxygenase. The prediction of the roles of different amino acids in 14DM is based on high resolution tertiary structures of these enzymes which set the stage for detailed understanding of the 14α-demethylase reaction and its selective, phyla-specific inhibition which is crucial for the design of potent inhibitors for treatment of infection by pathogenic microbes.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Waterman MR, Lepesheva GI. Sterol 14 alpha-demethylase, an abundant and essential mixed-function oxidase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005;338:418–422. - PubMed
-
- Waterman MR. Production of Sex Steroids. In: Huges IA, editor. Frontiers in Endocrinology Sex Differentiation: Clinical and Biological Aspects, Sex Differentiation: Clinical and Biological Aspects, V20-Serono Symposia Series. Christengraf, via Anagnina, Rome, Italy: 1996. pp. 61–69.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

