Epstein-Barr virus in bone marrow of rheumatoid arthritis patients predicts response to rituximab treatment
- PMID: 20547657
- PMCID: PMC2936947
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keq159
Epstein-Barr virus in bone marrow of rheumatoid arthritis patients predicts response to rituximab treatment
Abstract
Objectives: Viruses may contribute to RA. This prompted us to monitor viral load and response to anti-CD20 therapy in RA patients.
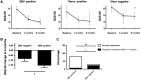
Methods: Blood and bone marrow from 35 RA patients were analysed for CMV, EBV, HSV-1, HSV-2, parvovirus B19 and polyomavirus using real-time PCR before and 3 months after rituximab (RTX) treatment and related to the levels of autoantibodies and B-cell depletion. Clinical response to RTX was defined as decrease in the 28-joint disease activity score (DAS-28) >1.3 at 6 months.
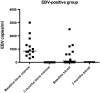
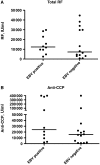
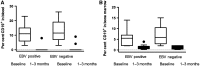
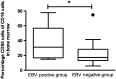
Results: Before RTX treatment, EBV was identified in 15 out of 35 patients (EBV-positive group), of which 4 expressed parvovirus. Parvovirus was further detected in eight patients (parvo-positive group). Twelve patients were negative for the analysed viruses. Following RTX, EBV was cleared, whereas parvovirus was unaffected. Eighteen patients were responders, of which 12 were EBV positive. The decrease in the DAS-28 was significantly higher in EBV-positive group compared with parvo-positive group (P = 0.002) and virus-negative patients (P = 0.04). Most of EBV-negative patients that responded to RTX (75%) required retreatment within the following 11 months compared with only 8% of responding EBV-positive patients. A decrease of RF, Ig-producing cells and CD19(+) B cells was observed following RTX but did not distinguish between viral infections. However, EBV-infected patients had significantly higher levels of Fas-expressing B cells at baseline as compared with EBV-negative groups.
Conclusions: EBV and parvovirus genomes are frequently found in bone marrow of RA patients. The presence of EBV genome was associated with a better clinical response to RTX. Thus, presence of EBV genome may predict clinical response to RTX.
Figures
References
-
- Franssila R, Hedman K. Infection and musculoskeletal conditions: viral causes of arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2006;20:1139–57. - PubMed
-
- Toussirot E, Roudier J. Epstein-Barr virus in autoimmune diseases. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2008;22:883–96. - PubMed
-
- Denman AM, Pelton BK, Hylton W, Palmer RG, Topper R. Herpes simplex virus and the rheumatic diseases. Rheumatol Int. 1989;9:143–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

