Zinc finger protein Gfi1 controls the endotoxin-mediated Toll-like receptor inflammatory response by antagonizing NF-kappaB p65
- PMID: 20547752
- PMCID: PMC2916436
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00087-10
Zinc finger protein Gfi1 controls the endotoxin-mediated Toll-like receptor inflammatory response by antagonizing NF-kappaB p65
Abstract
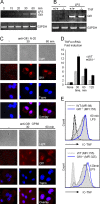
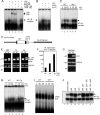
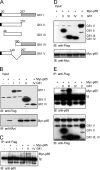
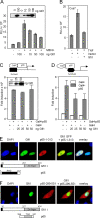
Endotoxin (bacterial lipopolysaccharide [LPS]) causes fatal septic shock via the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR-4) protein present on innate immunity effector cells, which activates nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB), inducing proinflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha). An early step in this process involves nuclear sequestration of the p65-RelA NF-kappaB subunit, enabling transcriptional activation of target inflammatory cytokine genes. Here, we analyzed the role of the nuclear zinc finger protein Gfi1 in the TLR response using primary bone marrow-derived macrophages. We show that upon LPS stimulation, expression of Gfi1 is induced with kinetics similar to those of nuclear translocation of p65 and that Gfi1 interacts with p65 and inhibits p65-mediated transcriptional transactivation by interfering with p65 binding to target gene promoter DNA. Gfi1-deficient macrophages show abnormally high mRNA levels of the TNF-alpha gene and many other p65 target genes and a higher rate of TNF promoter occupancy by p65 than wild-type cells after LPS stimulation, suggesting that Gfi1 functions as an antagonist of NF-kappaB activity at the level of promoter binding. Our findings identify a new function of Gfi1 as a general negative regulator of the endotoxin-initiated innate immune responses, including septic shock and possibly other severe inflammatory diseases.
Figures




References
-
- Akira, S., and K. Takeda. 2004. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4:499-511. - PubMed
-
- Akira, S., K. Takeda, and T. Kaisho. 2001. Toll-like receptors: critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2:675-680. - PubMed
-
- Beutler, B., and E. T. Rietschel. 2003. Innate immune sensing and its roots: the story of endotoxin. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3:169-176. - PubMed
-
- Blouin, C. C., E. L. Page, G. M. Soucy, and D. E. Richard. 2004. Hypoxic gene activation by lipopolysaccharide in macrophages: implication of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Blood 103:1124-1130. - PubMed
-
- Burns, K., J. Clatworthy, L. Martin, F. Martinon, C. Plumpton, B. Maschera, A. Lewis, K. Ray, J. Tschopp, and F. Volpe. 2000. Tollip, a new component of the IL-1RI pathway, links IRAK to the IL-1 receptor. Nat. Cell Biol. 2:346-351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
