The interaction of Epac1 and Ran promotes Rap1 activation at the nuclear envelope
- PMID: 20547757
- PMCID: PMC2916442
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00242-10
The interaction of Epac1 and Ran promotes Rap1 activation at the nuclear envelope
Abstract
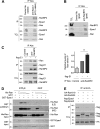
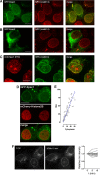
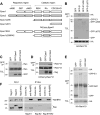
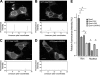
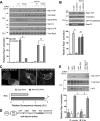
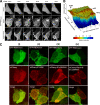
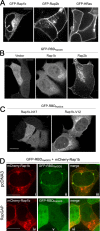
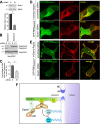
Epac1 (exchange protein directly activated by cyclic AMP [cAMP]) couples intracellular cAMP to the activation of Rap1, a Ras family GTPase that regulates cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation. Using mass spectrometry, we identified the small G protein Ran and Ran binding protein 2 (RanBP2) as potential binding partners of Epac1. Ran is a small G protein best known for its role in nuclear transport and can be found at the nuclear pore through its interaction with RanBP2. Here we demonstrate that Ran-GTP and Epac1 interact with each other in vivo and in vitro. This binding requires a previously uncharacterized Ras association (RA) domain in Epac1. Surprisingly, the interaction of Epac1 with Ran is necessary for the efficient activation of Rap1 by Epac1. We propose that Ran and RanBP2 anchor Epac1 to the nuclear pore, permitting cAMP signals to activate Rap1 at the nuclear envelope.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A SUMO-interacting motif in the guanine nucleotide exchange factor EPAC1 is required for subcellular targeting and function.J Biol Chem. 2025 Jun;301(6):110279. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110279. Epub 2025 May 22. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40412525 Free PMC article.
-
Rap1-mediated activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases by cyclic AMP is dependent on the mode of Rap1 activation.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Mar;26(6):2130-45. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.6.2130-2145.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16507992 Free PMC article.
-
MAP1A light chain 2 interacts with exchange protein activated by cyclic AMP 1 (EPAC1) to enhance Rap1 GTPase activity and cell adhesion.J Biol Chem. 2005 Mar 4;280(9):8109-16. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413697200. Epub 2004 Dec 9. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15591041
-
Lysine-acetylation as a fundamental regulator of Ran function: Implications for signaling of proteins of the Ras-superfamily.Small GTPases. 2015 Oct 2;6(4):189-95. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2015.1103399. Epub 2015 Oct 27. Small GTPases. 2015. PMID: 26507377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rap1 GTPases: an emerging role in the cardiovasculature.Life Sci. 2011 Apr 11;88(15-16):645-52. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2011.01.023. Epub 2011 Feb 2. Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 21295042 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The nucleoporin RanBP2 tethers the cAMP effector Epac1 and inhibits its catalytic activity.J Cell Biol. 2011 Jun 13;193(6):1009-20. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201011126. J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21670213 Free PMC article.
-
A SUMO-interacting motif in the guanine nucleotide exchange factor EPAC1 is required for subcellular targeting and function.J Biol Chem. 2025 Jun;301(6):110279. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110279. Epub 2025 May 22. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40412525 Free PMC article.
-
A SUMO-interacting motif in the guanine nucleotide exchange factor EPAC1 is required for subcellular targeting and function.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 3:2025.05.02.651912. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.02.651912. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: J Biol Chem. 2025 Jun;301(6):110279. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110279. PMID: 40654774 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Radixin assembles cAMP effectors Epac and PKA into a functional cAMP compartment: role in cAMP-dependent cell proliferation.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 7;286(1):859-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.163816. Epub 2010 Nov 3. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21047789 Free PMC article.
-
Role of exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (EPAC1) in breast cancer cell migration and apoptosis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2017 Jun;430(1-2):115-125. doi: 10.1007/s11010-017-2959-3. Epub 2017 Feb 16. Mol Cell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28210903
References
-
- Baillie, G. S. 2009. Compartmentalized signalling: spatial regulation of cAMP by the action of compartmentalized phosphodiesterases. FEBS J. 276:1790-1799. - PubMed
-
- Bivona, T. G., and M. R. Philips. 2005. Analysis of Ras and Rap activation in living cells using fluorescent Ras binding domains. Methods Enzymol. 37:138-145. - PubMed
-
- Bolger, G. B., G. S. Baillie, X. Li, M. J. Lynch, P. Herzyk, A. Mohamed, L. H. Mitchell, A. McCahill, C. Hundsrucker, E. Klussmann, D. R. Adams, and M. D. Houslay. 2006. Scanning peptide array analyses identify overlapping binding sites for the signalling scaffold proteins, beta-arrestin and RACK1, in cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase PDE4D5. Biochem. J. 398:23-36. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
