Influence of heparin mimetics on assembly of the FGF.FGFR4 signaling complex
- PMID: 20547770
- PMCID: PMC2924102
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.095109
Influence of heparin mimetics on assembly of the FGF.FGFR4 signaling complex
Abstract
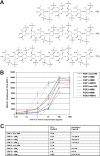
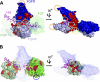
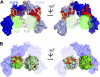
Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling regulates mammalian development and metabolism, and its dysregulation is implicated in many inherited and acquired diseases, including cancer. Heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycans (HSGAGs) are essential for FGF signaling as they promote FGF.FGF receptor (FGFR) binding and dimerization. Using novel organic synthesis protocols to prepare homogeneously sulfated heparin mimetics (HM), including hexasaccharide (HM(6)), octasaccharide (HM(8)), and decasaccharide (HM(10)), we tested the ability of these HM to support FGF1 and FGF2 signaling through FGFR4. Biological assays show that both HM(8) and HM(10) are significantly more potent than HM(6) in promoting FGF2-mediated FGFR4 signaling. In contrast, all three HM have comparable activity in promoting FGF1.FGFR4 signaling. To understand the molecular basis for these differential activities in FGF1/2.FGFR4 signaling, we used NMR spectroscopy, isothermal titration calorimetry, and size-exclusion chromatography to characterize binding interactions of FGF1/2 with the isolated Ig-domain 2 (D2) of FGFR4 in the presence of HM, and binary interactions of FGFs and D2 with HM. Our data confirm the existence of both a secondary FGF1.FGFR4 interaction site and a direct FGFR4.FGFR4 interaction site thus supporting the formation of the symmetric mode of FGF.FGFR dimerization in solution. Moreover, our results show that the observed higher activity of HM(8) relative to HM(6) in stimulating FGF2.FGFR4 signaling correlates with the higher affinity of HM(8) to bind and dimerize FGF2. Notably FGF2.HM(8) exhibits pronounced positive binding cooperativity. Based on our findings we propose a refined symmetric FGF.FGFR dimerization model, which incorporates the differential ability of HM to dimerize FGFs.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

