Improved IL-2 immunotherapy by selective stimulation of IL-2 receptors on lymphocytes and endothelial cells
- PMID: 20547866
- PMCID: PMC2900642
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1002569107
Improved IL-2 immunotherapy by selective stimulation of IL-2 receptors on lymphocytes and endothelial cells
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jan 3;109(1):345
Abstract
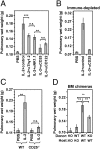
IL-2 immunotherapy is an attractive treatment option for certain metastatic cancers. However, administration of IL-2 to patients can lead, by ill-defined mechanisms, to toxic adverse effects including severe pulmonary edema. Here, we show that IL-2-induced pulmonary edema is caused by direct interaction of IL-2 with functional IL-2 receptors (IL-2R) on lung endothelial cells in vivo. Treatment of mice with high-dose IL-2 led to efficient expansion of effector immune cells expressing high levels of IL-2Rbetagamma, including CD8(+) T cells and natural killer cells, which resulted in a considerable antitumor response against s.c. and pulmonary B16 melanoma nodules. However, high-dose IL-2 treatment also affected immune cell lineage marker-negative CD31(+) pulmonary endothelial cells via binding to functional alphabetagamma IL-2Rs, expressed at low to intermediate levels on these cells, thus causing pulmonary edema. Notably, IL-2-mediated pulmonary edema was abrogated by a blocking antibody to IL-2Ralpha (CD25), genetic disruption of CD25, or the use of IL-2Rbetagamma-directed IL-2/anti-IL-2 antibody complexes, thereby interfering with IL-2 binding to IL-2Ralphabetagamma(+) pulmonary endothelial cells. Moreover, IL-2/anti-IL-2 antibody complexes led to vigorous activation of IL-2Rbetagamma(+) effector immune cells, which generated a dramatic antitumor response. Thus, IL-2/anti-IL-2 antibody complexes might improve current strategies of IL-2-based tumor immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: O.B. is a shareholder of Nascent Biologics Inc.
Figures




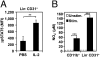
References
-
- Malek TR. The biology of interleukin-2. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:453–479. - PubMed
-
- Boyman O, Purton JF, Surh CD, Sprent J. Cytokines and T-cell homeostasis. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007;19:320–326. - PubMed
-
- Minami Y, Kono T, Miyazaki T, Taniguchi T. The IL-2 receptor complex: Its structure, function, and target genes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:245–268. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, Itoh M, Toda M. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. J Immunol. 1995;155:1151–1164. - PubMed
-
- Lefrancois L, Klein JR, Paetkau V, Bevan MJ. Antigen-independent activation of memory cytotoxic T cells by interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1984;132:1845–1850. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

