Kinesin's light chains inhibit the head- and microtubule-binding activity of its tail
- PMID: 20547877
- PMCID: PMC2900695
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1005854107
Kinesin's light chains inhibit the head- and microtubule-binding activity of its tail
Abstract
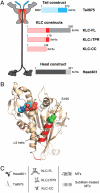
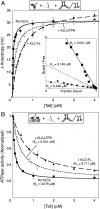
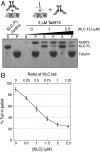
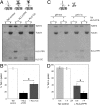
Kinesin-1 is a microtubule-based motor comprising two heavy chains (KHCs) and two light chains (KLCs). Motor activity is precisely regulated to avoid futile ATP consumption and to ensure proper intracellular localization of kinesin-1 and its cargoes. The KHC tail inhibits ATPase activity by interacting with the enzymatic KHC heads, and the tail also binds microtubules. Here, we present a role for the KLCs in regulating both the head- and microtubule-binding activities of the kinesin-1 tail. We show that KLCs reduce the affinity of the head-tail interaction over tenfold and concomitantly repress the tail's regulatory activity. We also show that KLCs inhibit tail-microtubule binding by a separate mechanism. Inhibition of head-tail binding requires steric and electrostatic factors. Inhibition of tail-microtubule binding is largely electrostatic, pH dependent, and mediated partly by a highly negatively charged linker region between the KHC-interacting and cargo-binding domains of the KLCs. Our data support a model wherein KLCs promote activation of kinesin-1 for cargo transport by simultaneously suppressing tail-head and tail-microtubule interactions. KLC-mediated inhibition of tail-microtubule binding may also influence diffusional movement of kinesin-1 on microtubules, and kinesin-1's role in microtubule transport/sliding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SKIP controls lysosome positioning using a composite kinesin-1 heavy and light chain-binding domain.J Cell Sci. 2017 May 1;130(9):1637-1651. doi: 10.1242/jcs.198267. Epub 2017 Mar 16. J Cell Sci. 2017. PMID: 28302907 Free PMC article.
-
Microtubule-associated protein-like binding of the kinesin-1 tail to microtubules.J Biol Chem. 2010 Mar 12;285(11):8155-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.068247. Epub 2010 Jan 12. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20071331 Free PMC article.
-
The C-terminal region of the stalk domain of ubiquitous human kinesin heavy chain contains the binding site for kinesin light chain.Biochemistry. 1998 Nov 24;37(47):16663-70. doi: 10.1021/bi981163r. Biochemistry. 1998. PMID: 9843434
-
Review: regulation mechanisms of Kinesin-1.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2006;27(2):153-60. doi: 10.1007/s10974-005-9054-1. Epub 2006 Feb 1. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2006. PMID: 16450053 Review.
-
A look into kinesin's powerhouse.FEBS Lett. 2001 Nov 23;508(3):291-4. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)03064-2. FEBS Lett. 2001. PMID: 11728437 Review.
Cited by
-
The structure of the kinesin-1 motor-tail complex reveals the mechanism of autoinhibition.Science. 2011 Aug 12;333(6044):883-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1204824. Science. 2011. PMID: 21836017 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of conventional kinesin motors in clusters by Shaw voltage-gated K+ channels.J Cell Sci. 2013 May 1;126(Pt 9):2027-41. doi: 10.1242/jcs.122234. Epub 2013 Mar 13. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23487040 Free PMC article.
-
Role of kinesin-1-based microtubule sliding in Drosophila nervous system development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Aug 23;113(34):E4985-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1522416113. Epub 2016 Aug 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27512046 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for power stroke vs. Brownian ratchet mechanisms of motor proteins.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Oct 1;116(40):19777-19785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1818589116. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31506355 Free PMC article.
-
SKIP controls lysosome positioning using a composite kinesin-1 heavy and light chain-binding domain.J Cell Sci. 2017 May 1;130(9):1637-1651. doi: 10.1242/jcs.198267. Epub 2017 Mar 16. J Cell Sci. 2017. PMID: 28302907 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hook P, Vallee RB. The dynein family at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:4369–4371. - PubMed
-
- O’Connell CB, Tyska MJ, Mooseker MS. Myosin at work: Motor adaptations for a variety of cellular functions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1773:615–630. - PubMed
-
- Hirokawa N, Noda Y, Tanaka Y, Niwa S. Kinesin superfamily motor proteins and intracellular transport. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10:682–696. - PubMed
-
- Verhey KJ, Hammond JW. Traffic control: Regulation of kinesin motors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10:765–777. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

