Brain insulin action regulates hypothalamic glucose sensing and the counterregulatory response to hypoglycemia
- PMID: 20547974
- PMCID: PMC2927950
- DOI: 10.2337/db10-0401
Brain insulin action regulates hypothalamic glucose sensing and the counterregulatory response to hypoglycemia
Abstract
Objective: An impaired ability to sense and appropriately respond to insulin-induced hypoglycemia is a common and serious complication faced by insulin-treated diabetic patients. This study tests the hypothesis that insulin acts directly in the brain to regulate critical glucose-sensing neurons in the hypothalamus to mediate the counterregulatory response to hypoglycemia.
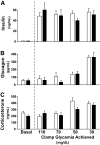
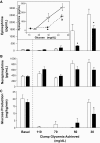
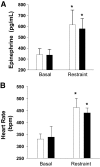
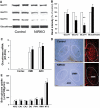
Research design and methods: To delineate insulin actions in the brain, neuron-specific insulin receptor knockout (NIRKO) mice and littermate controls were subjected to graded hypoglycemic (100, 70, 50, and 30 mg/dl) hyperinsulinemic (20 mU/kg/min) clamps and nonhypoglycemic stressors (e.g., restraint, heat). Subsequently, counterregulatory responses, hypothalamic neuronal activation (with transcriptional marker c-fos), and regional brain glucose uptake (via (14)C-2deoxyglucose autoradiography) were measured. Additionally, electrophysiological activity of individual glucose-inhibited neurons and hypothalamic glucose sensing protein expression (GLUTs, glucokinase) were measured.
Results: NIRKO mice revealed a glycemia-dependent impairment in the sympathoadrenal response to hypoglycemia and demonstrated markedly reduced (3-fold) hypothalamic c-fos activation in response to hypoglycemia but not other stressors. Glucose-inhibited neurons in the ventromedial hypothalamus of NIRKO mice displayed significantly blunted glucose responsiveness (membrane potential and input resistance responses were blunted 66 and 80%, respectively). Further, hypothalamic expression of the insulin-responsive GLUT 4, but not glucokinase, was reduced by 30% in NIRKO mice while regional brain glucose uptake remained unaltered.
Conclusions: Chronically, insulin acts in the brain to regulate the counterregulatory response to hypoglycemia by directly altering glucose sensing in hypothalamic neurons and shifting the glycemic levels necessary to elicit a normal sympathoadrenal response.
Figures



Comment in
-
Highlights in basic autonomic neurosciences: autonomic control of the counter-regulatory response and glucose homeostasis.Auton Neurosci. 2012 Jul 2;169(1):1-3. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2012.04.002. Epub 2012 May 9. Auton Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22578333 No abstract available.
References
-
- Epidemiology of severe hypoglycemia in the diabetes control and complications trial. The DCCT Research Group. Am J Med 1991;90:450–459 - PubMed
-
- Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet 1998;352:837–853 - PubMed
-
- Laing SP, Swerdlow AJ, Slater SD, Botha JL, Burden AC, Waugh NR, Smith AW, Hill RD, Bingley PJ, Patterson CC, Qiao Z, Keen H. The British Diabetic Association Cohort Study, II. cause-specific mortality in patients with insulin-treated diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 1999;16:466–471 - PubMed
-
- Cryer PE, Davis SN, Shamoon H. Hypoglycemia in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2003;26:1902–1912 - PubMed
-
- Jones TW, Davis EA. Hypoglycemia in children with type 1 diabetes: current issues and controversies. Pediatr Diabetes 2003;4:143–150 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R56 DK055619/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DK084813/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-55619/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK073683/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK-056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK081358/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK055619/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1F31-DK-084813/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK081538/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-073683/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-081358/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

