Ablation of 4E-BP1/2 prevents hyperglycemia-mediated induction of VEGF expression in the rodent retina and in Muller cells in culture
- PMID: 20547975
- PMCID: PMC2927931
- DOI: 10.2337/db10-0148
Ablation of 4E-BP1/2 prevents hyperglycemia-mediated induction of VEGF expression in the rodent retina and in Muller cells in culture
Abstract
Objective: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) contributes to diabetic retinopathy, but control of its expression is not well understood. Here, we tested the hypothesis that hyperglycemia mediates induction of VEGF expression in a eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) binding protein (4E-BP) 1 and 2 dependent manner.
Research design and methods: The retina was harvested from control and type 1 diabetic rats and mice and analyzed for VEGF mRNA and protein expression as well as biomarkers of translational control mechanisms. Similar analyses were performed in Müller cell cultures exposed to hyperglycemic conditions. The effect of 4E-BP1 and 4E-BP2 gene deletion on VEGF expression was examined in mice and in mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEFs).
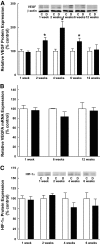
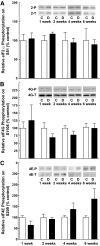
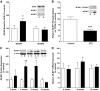
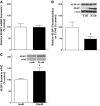
Results: Whereas VEGF mRNA in the retina remained constant, VEGF expression was increased as early as 2 weeks after the onset of diabetes. Increases in expression of 4E-BP1 protein mirrored those of VEGF and expression of 4E-BP1 mRNA was unchanged. Similar results were observed after 10 h of exposure of cells in culture to hyperglycemic conditions. Importantly, the diabetes-induced increase in VEGF expression was not observed in mice deficient in 4E-BP1 and 4E-BP2, nor in MEFs lacking the two proteins.
Conclusions: Hyperglycemia induces VEGF expression through cap-independent mRNA translation mediated by increased expression of 4E-BP1. Because the VEGF mRNA contains two internal ribosome entry sites, the increased expression is likely a consequence of ribosome loading at these sites. These findings provide new insights into potential targets for treatment of diabetic retinopathy.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Regulated in development and DNA damage 1 is necessary for hyperglycemia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression in the retina of diabetic rodents.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 6;290(6):3865-74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.623058. Epub 2014 Dec 29. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25548280 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes enhances translation of Cd40 mRNA in murine retinal Müller glia via a 4E-BP1/2-dependent mechanism.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jul 31;295(31):10831-10841. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013711. Epub 2020 May 31. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32475820 Free PMC article.
-
The Translational Repressor 4E-BP1 Contributes to Diabetes-Induced Visual Dysfunction.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016 Mar;57(3):1327-37. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-18719. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016. PMID: 26998719 Free PMC article.
-
Eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 (4E-BP1): a master regulator of mRNA translation involved in tumorigenesis.Oncogene. 2016 Sep 8;35(36):4675-88. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.515. Epub 2016 Feb 1. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26829052 Review.
-
Translational control of immune responses: from transcripts to translatomes.Nat Immunol. 2014 Jun;15(6):503-11. doi: 10.1038/ni.2891. Nat Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24840981 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulated in development and DNA damage 1 is necessary for hyperglycemia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression in the retina of diabetic rodents.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 6;290(6):3865-74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.623058. Epub 2014 Dec 29. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25548280 Free PMC article.
-
Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitor-Mediated HIF Activation Drives Transcriptional Reprogramming in Retinal Pigment Epithelium: Relevance to Chronic Kidney Disease.Cells. 2025 Jul 21;14(14):1121. doi: 10.3390/cells14141121. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40710374 Free PMC article.
-
Glucosamine induces REDD1 to suppress insulin action in retinal Müller cells.Cell Signal. 2016 May;28(5):384-390. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.01.017. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Cell Signal. 2016. PMID: 26852666 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperglycemia mediates a shift from cap-dependent to cap-independent translation via a 4E-BP1-dependent mechanism.Diabetes. 2013 Jul;62(7):2204-14. doi: 10.2337/db12-1453. Epub 2013 Feb 22. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23434932 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes enhances translation of Cd40 mRNA in murine retinal Müller glia via a 4E-BP1/2-dependent mechanism.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jul 31;295(31):10831-10841. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013711. Epub 2020 May 31. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32475820 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saaddine JB, Honeycutt AA, Narayan KM, Zhang X, Klein R, Boyle JP. Projection of diabetic retinopathy and other major eye diseases among people with diabetes mellitus: United States, 2005–2050. Arch Ophthalmol 2008;126:1740–1747 - PubMed
-
- Adamis AP, Miller JW, Bernal MT, D'Amico DJ, Folkman J, Yeo TK, Yeo KT. Increased vascular endothelial growth factor levels in the vitreous of eyes with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 1994;118:445–450 - PubMed
-
- Aiello LM, Cavallerano J. Diabetic retinopathy. Curr Ther Endocrinol Metab 1994;5:436–446 - PubMed
-
- Aiello LP, Avery RL, Arrigg PG, Keyt BA, Jampel HD, Shah ST, Pasquale LR, Thieme H, Iwamoto MA, Park JE. Vascular endothelial growth factor in ocular fluid of patients with diabetic retinopathy and other retinal disorders. N Engl J Med 1994;331:1480–1487 - PubMed
-
- Miller JW, Adamis AP, Shima DT, D'Amore PA, Moulton RS, O'Reilly MS, Folkman J, Dvorak HF, Brown LF, Berse B. Vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor is temporally and spatially correlated with ocular angiogenesis in a primate model. Am J Pathol 1994;145:574–584 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

