Polymorphic human prostaglandin H synthase-2 proteins and their interactions with cyclooxygenase substrates and inhibitors
- PMID: 20548327
- PMCID: PMC4465550
- DOI: 10.1038/tpj.2010.49
Polymorphic human prostaglandin H synthase-2 proteins and their interactions with cyclooxygenase substrates and inhibitors
Abstract
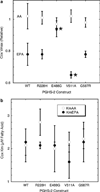
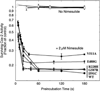
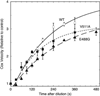
The cyclooxygenase (COX) activity of prostaglandin H synthase-2 (PGHS-2) is implicated in colorectal cancer and is targeted by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and dietary n-3 fatty acids. We used purified, recombinant proteins to evaluate the functional impacts of the R228H, E488G, V511A and G587R PGHS-2 polymorphisms on COX activity, fatty acid selectivity and NSAID actions. Compared to wild-type PGHS-2, COX activity with arachidonate was ∼20% lower in 488G and ∼20% higher in 511A. All variants showed time-dependent inhibition by the COX-2-specific inhibitor (coxib) nimesulide, but 488G and 511A had 30-60% higher residual COX activity; 511A also showed up to 70% higher residual activity with other time-dependent inhibitors. In addition, 488G and 511A differed significantly from wild type in Vmax values with the two fatty acids: 488G showed ∼20% less and 511A showed ∼20% more discrimination against eicosapentaenoic acid. The Vmax value for eicosapentaenoate was not affected in 228H or 587R, nor were the Km values or the COX activation efficiency (with arachidonate) significantly altered in any variant. Thus, the E488G and V511A PGHS-2 polymorphisms may predict who will most likely benefit from interventions with some NSAIDs or n-3 fatty acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

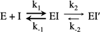
Similar articles
-
Pre-existent asymmetry in the human cyclooxygenase-2 sequence homodimer.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 4;288(40):28641-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.505503. Epub 2013 Aug 16. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23955344 Free PMC article.
-
Differential inhibition of murine prostaglandin synthase-1 and -2 by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs using exogenous and endogenous sources of arachidonic acid.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997 Feb;280(2):606-13. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997. PMID: 9023270
-
The role of arginine 120 of human prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthase-2 in the interaction with fatty acid substrates and inhibitors.J Biol Chem. 1999 Jun 11;274(24):17109-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.24.17109. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10358065
-
Selective inhibitors of COX-2.Agents Actions Suppl. 1995;46:159-68. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7276-8_16. Agents Actions Suppl. 1995. PMID: 7610986 Review.
-
Biochemistry of prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthase-1 and synthase-2 and their differential susceptibility to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.Semin Nephrol. 1995 May;15(3):179-94. Semin Nephrol. 1995. PMID: 7631045 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic variation in the lipoxygenase pathway and risk of colorectal neoplasia.Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2013 May;52(5):437-49. doi: 10.1002/gcc.22042. Epub 2013 Feb 12. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23404351 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased cyclooxygenase inhibition by aspirin in polymorphic variants of human prostaglandin H synthase-1.Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2012 Jul;22(7):525-37. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0b013e32835366f6. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22513397 Free PMC article.
-
Enzymes of the cyclooxygenase pathways of prostanoid biosynthesis.Chem Rev. 2011 Oct 12;111(10):5821-65. doi: 10.1021/cr2002992. Epub 2011 Sep 27. Chem Rev. 2011. PMID: 21942677 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
COX-1 (PTGS1) and COX-2 (PTGS2) polymorphisms, NSAID interactions, and risk of colon and rectal cancers in two independent populations.Cancer Causes Control. 2013 Dec;24(12):2059-75. doi: 10.1007/s10552-013-0282-1. Cancer Causes Control. 2013. PMID: 24022467 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith WL. Nutritionally essential fatty acids and biologically indispensable cyclooxygenases. Trends Biochem Sci. 2008;33:27–37. - PubMed
-
- Funk CD. Prostaglandins and leukotrienes: advances in eicosanoid biology. Science. 2001;294:1871–1875. - PubMed
-
- Simmons DL, Botting RM, Hla T. Cyclooxygenase isozymes: the biology of prostaglandin synthesis and inhibition. Pharmacol Rev. 2004;56:387–437. - PubMed
-
- Mann JR, DuBois RN. Cyclooxygenase-2 and gastrointestinal cancer. Cancer J. 2004;10:145–152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

