A case of diffuse neurofibroma of the scalp
- PMID: 20548855
- PMCID: PMC2883368
- DOI: 10.5021/ad.2009.21.1.46
A case of diffuse neurofibroma of the scalp
Abstract
A neurofibroma is a benign tumor of the peripheral nerve sheath characterized by proliferation of Schwann cells, perineural cells, and endoneurial fibroblasts. Different types of neurofibromas can be identified, including localized, plexiform, and diffuse types. Neurofibromas can involve any site on the body skin. The diffuse variant is rare and occurs primarily in children and young adults. It involves the skin and subcutaneous tissue in a plaque-like fashion on the head and neck regions. We present a case of a 10-year-old boy who had a diffuse neurofibroma on the scalp.
Keywords: Diffuse neurofibroma; Scalp.
Figures

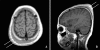

References
-
- Peh WC, Shek TW, Yip DK. Magnetic resonance imaging of subcutaneous diffuse neurofibroma. Br J Radiol. 1997;70:1180–1183. - PubMed
-
- Yang JS, Park HJ, Lee HJ, Baek SC, Byun DG. A case of trichotillomania associated with diffuse neurofibroma. Korean J Dermatol. 2001;39:1152–1156.
-
- Cha SH, Cho SH, Lee JD. A case of diffuse neurofibroma. Korean J Dermatol. 2008;46:355–358.
-
- Daoud MS, Pittelkow MR. Lichen planus. In: Freedberg IM, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, Austen KF, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, editors. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 6th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2003. pp. 463–477.
-
- van Zuuren EJ, Posma AN. Diffuse neurofibroma on the lower back. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:938–940. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

