A study on the hearing of children with non-syndromic cleft palate/lip
- PMID: 20549075
- PMCID: PMC9446030
- DOI: 10.1590/S1808-86942010000200004
A study on the hearing of children with non-syndromic cleft palate/lip
Abstract
Children with cleft lip/palate often present otitis media as a result of anatomic and/or functional alterations of the Eustachian tube.
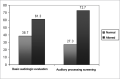
Aim: To analyze the results of Basic Audiologic Evaluation (BAE) and Auditory Processing Screening (APS) in children with cleft lip/palate.
Study design: Prospective cross-sectional cohort.
Materials and methods: Forty-four male and female children, within the 8 to 14 age range with non-syndromic cleft lip/palate, referred by the institution where the study was carried out. The BAE was made up by an interview, otoscopy, threshold tonal audiometry, logoaudiometry and impedance test. The APS was made up of 3 basic tests: Sound Localization Test, Sequential Memory for verbal and non-verbal sounds and Dichotic Listening Test.
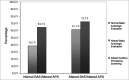
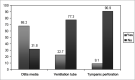
Results: The BAE revealed that 77.27% of the children presented normal hearing; 13.6% had conductive hearing loss and 2.2% presented mixed hearing loss. 21.2% of the children had type C tympanometry curve; 7.1% had a type B curve and 3.5% had an Ad curve. The APS was altered in 72.7% of the children and 45.5% of them presented altered results on the Dichotic Listening Test.
Conclusion: Children with cleft lip/palate had altered results on BAE and APS, which justifies audiological and medical follow-up.
Figures
References
-
- Sih T. In: 1a ed. Sih T., editor. Revinter; São Paulo: 1998. Complexo otite média; pp. 107–117. (Otorrinolaringologia pediátrica).
-
- Northern JL, Downs MP. Hearing in children. 3rd ed. Williams e Wilkens; Baltimore: 2002.
-
- Goudy S, Lott D, Canadyj, Smith RJ. Conductive hearing loss and otopathology in cleft palate patients. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;134(6):946–948. - PubMed
-
- Wyszynski D.F. Cleft Lip & Palate: from origin to treatment. University Press; New York, Oxford: 2002.
-
- Spina V, Psillakis JM, Lapa FS, Ferreira MC. Classificação das fissuras lábio-palatinas: sugestões de modificação. Rev Hosp Clín Fac Med S Paulo. 1972;27:5–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

