Major groove width variations in RNA structures determined by NMR and impact of 13C residual chemical shift anisotropy and 1H-13C residual dipolar coupling on refinement
- PMID: 20549304
- PMCID: PMC2929647
- DOI: 10.1007/s10858-010-9424-x
Major groove width variations in RNA structures determined by NMR and impact of 13C residual chemical shift anisotropy and 1H-13C residual dipolar coupling on refinement
Abstract
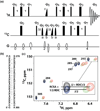
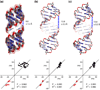
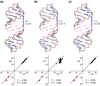
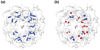
Ribonucleic acid structure determination by NMR spectroscopy relies primarily on local structural restraints provided by (1)H- (1)H NOEs and J-couplings. When employed loosely, these restraints are broadly compatible with A- and B-like helical geometries and give rise to calculated structures that are highly sensitive to the force fields employed during refinement. A survey of recently reported NMR structures reveals significant variations in helical parameters, particularly the major groove width. Although helical parameters observed in high-resolution X-ray crystal structures of isolated A-form RNA helices are sensitive to crystal packing effects, variations among the published X-ray structures are significantly smaller than those observed in NMR structures. Here we show that restraints derived from aromatic (1)H- (13)C residual dipolar couplings (RDCs) and residual chemical shift anisotropies (RCSAs) can overcome NMR restraint and force field deficiencies and afford structures with helical properties similar to those observed in high-resolution X-ray structures.
Figures



References
-
- Al-Hashimi HM. Beyond static structures of RNA by NMR: folding, refolding, and dynamics at atomic resolution. Biopolymers. 2007;86:345–347. - PubMed
-
- Al-Hashimi HM, Gorin A, Majumdar A, Patel DJ. Alignment of the HTLV-I Rex peptide bound to its target RNA aptamer from magnetic field-induced residual dipolar couplings and intermolecular hydrogen bonds. J Am Chem Soc. 2001a;123:3179–3180. - PubMed
-
- Al-Hashimi HM, Gosser Y, Gorin A, Hu W, Majumdar A, Patel DJ. Concerted motions in HIV-1 TAR RNA may allow access to bound state conformations: RNA dynamics from NMR residual dipolar couplings. J Mol Biol. 2002;315:95–102. - PubMed
-
- Al-Hashimi HM, Majumdar A, Gorin A, Kettani A, Skripkin E, Patel DJ. Field-and phage-induced dipolar couplings in a homodimeric DNA quadruplex: relative orientation of G.(C-A) triad and G-tetrad motifs and direct determination of C2 symmetry axis orientation. J Am Chem Soc. 2001b;123:633–640. - PubMed
-
- Al-Hashimi HM, Patel DJ. Residual dipolar couplings: synergy between NMR and structural genomics. J Biomol NMR. 2002;22:1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

