Efficacy of celecoxib, meloxicam and paracetamol in elderly Kashin-Beck disease (KBD) patients
- PMID: 20549501
- PMCID: PMC3167448
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-010-1062-0
Efficacy of celecoxib, meloxicam and paracetamol in elderly Kashin-Beck disease (KBD) patients
Abstract
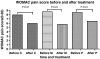
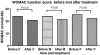
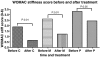
The objective of this study was to compare the efficacy and tolerability of celecoxib, meloxicam and paracetamol in late Kashin-Beck disease. Adults (n = 168) with Kashin-Beck disease were randomised in clusters to receive six week courses of celecoxib 200 mg once daily, meloxicam 7.5 mg once daily or paracetamol 300 mg three times daily. Efficacy assessments included overall joint pain intensity and Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index subscales; tolerability was evaluated by adverse event and physician reporting. Celecoxib and meloxicam were efficacious in relieving pain and improving stiffness, but unable to improve physical function after six weeks. Paracetamol was efficacious in relieving pain, but unable to improve morning stiffness and physical function after six weeks. Celecoxib and meloxicam provide predictable and sustained relief from pain and stiffness. Paracetamol can relieve the pain. None of the treatments improved impaired physical function in Kashin-Beck disease.
Figures
References
-
- Wang Y, Yang Z, Gilula LA, Zhu C. Kashin-Beck disease: radiographic appearance in the hands and wrists. Radiology. 1996;201:265–270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

