Sensing the fuels: glucose and lipid signaling in the CNS controlling energy homeostasis
- PMID: 20549539
- PMCID: PMC2933848
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-010-0414-7
Sensing the fuels: glucose and lipid signaling in the CNS controlling energy homeostasis
Abstract
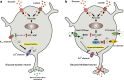
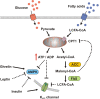
The central nervous system (CNS) is capable of gathering information on the body's nutritional state and it implements appropriate behavioral and metabolic responses to changes in fuel availability. This feedback signaling of peripheral tissues ensures the maintenance of energy homeostasis. The hypothalamus is a primary site of convergence and integration for these nutrient-related feedback signals, which include central and peripheral neuronal inputs as well as hormonal signals. Increasing evidence indicates that glucose and lipids are detected by specialized fuel-sensing neurons that are integrated in these hypothalamic neuronal circuits. The purpose of this review is to outline the current understanding of fuel-sensing mechanisms in the hypothalamus, to integrate the recent findings in this field, and to address the potential role of dysregulation in these pathways in the development of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figures
References
-
- Bernard C. Leçons de physiologie experimentale appliquée à la medecine. Baillère et Fils Paris. 1855;2:296–313.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

