Reelin expression during embryonic development of the pig brain
- PMID: 20550682
- PMCID: PMC2895594
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-11-75
Reelin expression during embryonic development of the pig brain
Abstract
Background: Reelin is an extracellular glycoprotein of crucial importance in the developmental organisation of neurons in the mammalian cerebral cortex and other laminated brain regions. The pig possesses a gyrencephalic brain that bears resemblance to the human brain. In order to establish an animal model for neuronal migration disorders in the pig, we have studied the expression pattern and structure of Reelin during pig brain development.
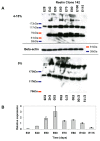
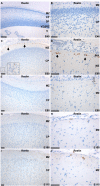
Results: We determined the sequence of pig Reelin mRNA and protein and identified a high degree of homology to human Reelin. A peak in Reelin mRNA and protein expression is present during the period of major neurogenesis and neuronal migration. This resembles observations for human brain development. Immunohistochemical analysis showed the highest expression of Reelin in the Cajal-Reztius cells of the marginal zone, in resemblance with observations for the developing brain in humans and other mammalian species.
Conclusions: We conclude that the pig might serve as an alternative animal model to study Reelin functions and that manipulation of the pig Reelin could allow the establishment of an animal model for human neuronal migration disorders.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

