Genomes of three tomato pathogens within the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex reveal significant evolutionary divergence
- PMID: 20550686
- PMCID: PMC2900269
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-379
Genomes of three tomato pathogens within the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex reveal significant evolutionary divergence
Abstract
Background: The Ralstonia solanacearum species complex includes thousands of strains pathogenic to an unusually wide range of plant species. These globally dispersed and heterogeneous strains cause bacterial wilt diseases, which have major socio-economic impacts. Pathogenicity is an ancestral trait in R. solanacearum and strains with high genetic variation can be subdivided into four phylotypes, correlating to isolates from Asia (phylotype I), the Americas (phylotype IIA and IIB), Africa (phylotype III) and Indonesia (phylotype IV). Comparison of genome sequences strains representative of this phylogenetic diversity can help determine which traits allow this bacterium to be such a pathogen of so many different plant species and how the bacteria survive in many different habitats.
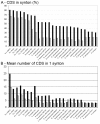
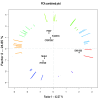
Results: The genomes of three tomato bacterial wilt pathogens, CFBP2957 (phy. IIA), CMR15 (phy. III) and PSI07 (phy. IV) were sequenced and manually annotated. These genomes were compared with those of three previously sequenced R. solanacearum strains: GMI1000 (tomato, phy. I), IPO1609 (potato, phy. IIB), and Molk2 (banana, phy. IIB). The major genomic features (size, G+C content, number of genes) were conserved across all of the six sequenced strains. Despite relatively high genetic distances (calculated from average nucleotide identity) and many genomic rearrangements, more than 60% of the genes of the megaplasmid and 70% of those on the chromosome are syntenic. The three new genomic sequences revealed the presence of several previously unknown traits, probably acquired by horizontal transfers, within the genomes of R. solanacearum, including a type IV secretion system, a rhi-type anti-mitotic toxin and two small plasmids. Genes involved in virulence appear to be evolving at a faster rate than the genome as a whole.
Conclusions: Comparative analysis of genome sequences and gene content confirmed the differentiation of R. solanacearum species complex strains into four phylotypes. Genetic distances between strains, in conjunction with CGH analysis of a larger set of strains, revealed differences great enough to consider reclassification of the R. solanacearum species complex into three species. The data are still too fragmentary to link genomic classification and phenotypes, but these new genome sequences identify a pan-genome more representative of the diversity in the R. solanancearum species complex.
Figures





References
-
- Yabuuchi E, Kosako Y, Yano I, Hotta H, Nishiuchi Y. Transfer of two Burkholderia and an Alcaligenes species to Ralstonia gen. Nov.: Proposal of Ralstonia pickettii (Ralston, Palleroni and Doudoroff 1973) comb. Nov., Ralstonia solanacearum (Smith 1896) comb. Nov. and Ralstonia eutropha (Davis 1969) comb. Nov. Microbiol Immunol. 1995;39:897–904. - PubMed
-
- Hayward AC. Characterristics of Pseudomonas solanacearum. J Appl Bacteriol. 1964;27:265–277.
-
- Buddenhagen I, Kelman A. Biological and physiological aspects of bacterial wilt caused by Pseudomonas solanacearum. Annual Review of Phytopathology. 1964;2:203–230. doi: 10.1146/annurev.py.02.090164.001223. - DOI
-
- Elphinstone JG. In: Bacterial Wilt: The Disease and the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex. Allen C, Prior P, Hayward AC, editor. St. Paul, Mn, USA: APS Press; 2005. The current bacterial wilt situation: A global overview.
-
- Janse JD, van den Beld HE, Elphinstone J, Simpkins S, Tjou-Tam-Sin NAA, van Vaerenbergh J. Introduction to Europe of Ralstonia solanacearum biovar 2, race 3 in Pelargonium zonale cuttings. J Plant Pathol. 2004;86:147–155.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

