Early clinical experience of radiotherapy of prostate cancer with volumetric modulated arc therapy
- PMID: 20550722
- PMCID: PMC2902493
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-5-54
Early clinical experience of radiotherapy of prostate cancer with volumetric modulated arc therapy
Abstract
Background: To report about initial clinical experience in radiation treatment of carcinoma of prostate with volumetric modulated arcs with the RapidArc (RA) technology.
Methods: Forty-five patients with a median age of 72 +/- 3, affected by prostate carcinoma (T1c: 22 patients, T2a-b: 17 patients, T3a-b: 6 patients. N0: 43 patients, N1-Nx: 2 patients, all M0), with initial PSA of 10.0 +/- 3.0 ng/mL, were treated with RapidArc in a feasibility study. All patients were treated with single arc using 6MV photons. Dose prescription ranged between 76 (7 patients) and 78 Gy (38 patients) in 2 Gy/fraction. Plan quality was assessed by means of Dose Volume Histogram (DVH) analysis. Technical parameters of arcs and pre-treatment quality assurance results (Gamma Agreement Index, GAI) are reported to describe delivery features. Early toxicity was scored (according to the Common Terminology Criteria of Adverse Effects scale, CTCAE, scale) at the end of treatment together with biochemical outcome (PSA).
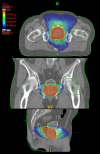
Results: From DVH data, target coverage was fulfilling planning objectives: V95% was in average higher than 98% and V107% approximately 0.0% (D2% approximately 104.0% in average). Homogeneity D5%-D95% ranged between 6.2 +/- 1.0% to 6.7 +/- 1.3%. For rectum, all planning objectives were largely met (e.g. V70Gy = 10.7 +/- 5.5% against an objective of < 25%) similarly for bladder (e.g. D2% = 79.4 +/- 1.2 Gy against an objective of 80.0 Gy). Maximum dose to femurs was D2% = 36.7 +/- 5.4 Gy against an objective of 47 Gy. Monitor Units resulted: MU/Gy = 239 +/- 37. Average beam on time was 1.24 +/- 0.0 minutes. Pre-treatment GAI resulted in 98.1 +/- 1.1%. Clinical data were recorded as PSA at 6 weeks after RT, with median values of 0.4 +/- 0.4 ng/mL. Concerning acute toxicity, no patient showed grade 2-3 rectal toxicity; 5/42 (12%) patients experienced grade 2 dysuria; 18/41 (44%) patients preserved complete or partial erectile function.
Conclusion: RapidArc proved to be a safe, qualitative and advantageous treatment modality for prostate cancer.
Figures

References
-
- NICER and FSO Statistics of Cancer Incidence: Switzerland 1983-2006. http://www.ti.ch/tumori
-
- Clivio A, Fogliata A, Franzetti-Pellanda A, Nicolini G, Vanetti E, Wyttenbach R, Cozzi L. Volumetric-modulated arc radiotherapy for carcinomas of the anal canal: A treatment planning comparison with fixed field IMRT. Radiother Oncol. 2009;92:118–124. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2008.12.020. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cozzi L, Dinshaw KA, Shrivastava SK, Mahantshetty U, Engineer R, Deshpande DD, Jamema SV, Vanetti E, Clivio A, Nicolini G, Fogliata A. A treatment planning study comparing volumetric arc modulation with RapidArc and fixed field IMRT for cervix uteri radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2008;89:180–191. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2008.06.013. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

