Confirmation of linkage to and localization of familial colon cancer risk haplotype on chromosome 9q22
- PMID: 20551049
- PMCID: PMC2896448
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0188
Confirmation of linkage to and localization of familial colon cancer risk haplotype on chromosome 9q22
Abstract
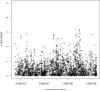
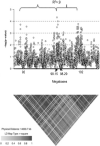
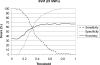
Genetic risk factors are important contributors to the development of colorectal cancer. Following the definition of a linkage signal at 9q22-31, we fine mapped this region in an independent collection of colon cancer families. We used a custom array of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) densely spaced across the candidate region, performing both single-SNP and moving-window association analyses to identify a colon neoplasia risk haplotype. Through this approach, we isolated the association effect to a five-SNP haplotype centered at 98.15 Mb on chromosome 9q. This haplotype is in strong linkage disequilibrium with the haplotype block containing HABP4 and may be a surrogate for the effect of this CD30 Ki-1 antigen. It is also in close proximity to GALNT12, also recently shown to be altered in colon tumors. We used a predictive modeling algorithm to show the contribution of this risk haplotype and surrounding candidate genes in distinguishing between colon cancer cases and healthy controls. The ability to replicate this finding, the strength of the haplotype association (odds ratio, 3.68), and the accuracy of our prediction model (approximately 60%) all strongly support the presence of a locus for familial colon cancer on chromosome 9q.
Copyright 2010 AACR.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Linkage analysis revealed risk loci on 6p21 and 18p11.2-q11.2 in familial colon and rectal cancer, respectively.Eur J Hum Genet. 2019 Aug;27(8):1286-1295. doi: 10.1038/s41431-019-0388-3. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Eur J Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 30952955 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-mapping of two differentiated thyroid carcinoma susceptibility loci at 9q22.33 and 14q13.3 detects novel candidate functional SNPs in Europeans from metropolitan France and Melanesians from New Caledonia.Int J Cancer. 2016 Aug 1;139(3):617-27. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30088. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Int J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26991144
-
Thyroid cancer susceptibility polymorphisms: confirmation of loci on chromosomes 9q22 and 14q13, validation of a recessive 8q24 locus and failure to replicate a locus on 5q24.J Med Genet. 2012 Mar;49(3):158-63. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2011-100586. Epub 2012 Jan 25. J Med Genet. 2012. PMID: 22282540 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive linkage and association analyses identify haplotype, near to the TNFSF15 gene, significantly associated with spondyloarthritis.PLoS Genet. 2009 Jun;5(6):e1000528. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000528. Epub 2009 Jun 19. PLoS Genet. 2009. PMID: 19543369 Free PMC article.
-
Localization of psoriasis-susceptibility locus PSORS1 to a 60-kb interval telomeric to HLA-C.Am J Hum Genet. 2000 Jun;66(6):1833-44. doi: 10.1086/302932. Epub 2000 May 5. Am J Hum Genet. 2000. PMID: 10801386 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Linkage analysis in familial non-Lynch syndrome colorectal cancer families from Sweden.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 11;8(12):e83936. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083936. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24349560 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Evidence for GALNT12 as a moderate penetrance gene for colorectal cancer.Hum Mutat. 2018 Aug;39(8):1092-1101. doi: 10.1002/humu.23549. Epub 2018 May 28. Hum Mutat. 2018. PMID: 29749045 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic predisposition to colorectal cancer: where we stand and future perspectives.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Aug 7;20(29):9828-49. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.9828. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25110415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aberrant O-glycosylation and anti-glycan antibodies in an autoimmune disease IgA nephropathy and breast adenocarcinoma.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Mar;70(5):829-39. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1082-6. Epub 2012 Aug 3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 22864623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hereditary and common familial colorectal cancer: evidence for colorectal screening.Dig Dis Sci. 2015 Mar;60(3):734-47. doi: 10.1007/s10620-014-3465-z. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Dig Dis Sci. 2015. PMID: 25501924 Review.
References
-
- Greenlee RT, Hill-Harmon MB, Murray T, Thun M. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2001;2001;51:15–36. - PubMed
-
- Skibber J, Minsky B, Hoff P, DeVita V, Hellman S, Rosenberg S. Cancer: Principles and practice of oncology. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; Philadelphia: 2001. Cancer of the colon. pp. 1216–71.
-
- Kinzler K, Vogelstein B. The Genetic Basis of Human Cancer. McGraw-Hill; New York: 2002. Colorectal tumors. pp. 583–612.
-
- Goss KH, Groden J. Biology of the adenomatous polyposis coli tumor suppressor. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:1967–79. - PubMed
-
- Marra G, Boland CR. Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer: the syndrome, the genes, and historical perspectives. J NatlCancer Inst. 1995;87:1114–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P41 RR003655/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA074799/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA104667/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA043703/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA074794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RR03655/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA097735/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA074783/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM28356/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA074806/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM028356/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA130901/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR053483/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA078296/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA074800/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

