Myc protein is stabilized by suppression of a novel E3 ligase complex in cancer cells
- PMID: 20551172
- PMCID: PMC2885659
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1920310
Myc protein is stabilized by suppression of a novel E3 ligase complex in cancer cells
Abstract
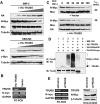
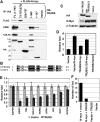
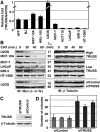
Rapid Myc protein turnover is critical for maintaining basal levels of Myc activity in normal cells and a prompt response to changing growth signals. We characterize a new Myc-interacting factor, TRPC4AP (transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 4-associated protein)/TRUSS (tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated ubiquitous scaffolding and signaling protein), which is the receptor for a DDB1 (damage-specific DNA-binding protein 1)-CUL4 (Cullin 4) E3 ligase complex for selective Myc degradation through the proteasome. TRPC4AP/TRUSS binds specifically to the Myc C terminus and promotes its ubiquitination and destruction through the recognition of evolutionarily conserved domains in the Myc N terminus. TRPC4AP/TRUSS suppresses Myc-mediated transactivation and transformation in a dose-dependent manner. Finally, we found that TRPC4AP/TRUSS expression is strongly down-regulated in most cancer cell lines, leading to Myc protein stabilization. These studies identify a novel pathway targeting Myc degradation that is suppressed in cancer cells.
Figures


Comment in
-
Tumorigenesis: Might as well face it, you're addicted to MYC.Nat Rev Cancer. 2010 Aug;10(8):532-3. doi: 10.1038/nrc2908. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20677353 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bazarov AV, Adachi S, Li SF, Mateyak MK, Wei S, Sedivy JM 2001. A modest reduction in c-myc expression has minimal effects on cell growth and apoptosis but dramatically reduces susceptibility to Ras and Raf transformation. Cancer Res 61: 1178–1186 - PubMed
-
- Bonvini P, Nguyen P, Trepel J, Neckers LM 1998. In vivo degradation of N-myc in neuroblastoma cells is mediated by the 26S proteasome. Oncogene 16: 1131–1139 - PubMed
-
- Cohn SL, Salwen H, Quasney MW, Ikegaki N, Cowan JM, Herst CV, Kennett RH, Rosen ST, DiGiuseppe JA, Brodeur GM 1990. Prolonged N-myc protein half-life in a neuroblastoma cell line lacking N-myc amplification. Oncogene 5: 1821–1827 - PubMed
-
- Cowling VH, Cole MD 2006. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by the Myc oncoproteins. Semin Cancer Biol 16: 242–252 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
