Economic evaluation of the HF-ACTION (Heart Failure: A Controlled Trial Investigating Outcomes of Exercise Training) randomized controlled trial: an exercise training study of patients with chronic heart failure
- PMID: 20551371
- PMCID: PMC3050585
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.109.907287
Economic evaluation of the HF-ACTION (Heart Failure: A Controlled Trial Investigating Outcomes of Exercise Training) randomized controlled trial: an exercise training study of patients with chronic heart failure
Abstract
Background: Heart Failure: A Controlled Trial Investigating Outcomes of Exercise Training (HF-ACTION) assigned 2331 outpatients with medically stable heart failure to exercise training or usual care. We compared medical resource use and costs incurred by these patients during follow-up.
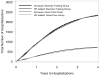
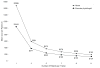
Methods and results: Extensive data on medical resource use and hospital bills were collected throughout the trial for estimates of direct medical costs. Intervention costs were estimated using patient-level trial data, administrative records, and published unit costs. Mean follow-up was 2.5 years. There were 2297 hospitalizations in the exercise group and 2332 in the usual care group (P=0.92). The mean number of inpatient days was 13.6 (standard deviation [SD], 27.0) in the exercise group and 15.0 (SD, 31.4) in the usual care group (P=0.23). Other measures of resource use were similar between groups, except for trends indicating that fewer patients in the exercise group underwent high-cost inpatient procedures. Total direct medical costs per participant were an estimated $50,857 (SD, $81,488) in the exercise group and $56,177 (SD, $92,749) in the usual care group (95% confidence interval for the difference, $-12,755 to $1547; P=0.10). The direct cost of exercise training was an estimated $1006 (SD, $337). Patient time costs were an estimated $5018 (SD, $4600).
Conclusions: The cost of exercise training was relatively low for the health care system, but patients incurred significant time costs. In this economic evaluation, there was little systematic benefit in terms of overall medical resource use with this intervention.
Clinical trial registration: URL: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT00047437.
Figures
References
-
- Curtis LH, Whellan DJ, Hammill BG, Hernandez AF, Anstrom KJ, Shea AM, Schulman KA. Incidence and prevalence of heart failure in elderly persons, 1994–2003. Arch Intern Med. 2008;168:418–424. - PubMed
-
- Loehr LR, Rosamond WD, Chang PP, Folsom AR, Chambless LE. Heart failure incidence and survival (from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study) Am J Cardiol. 2008;101:1016–1022. - PubMed
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M, De Simone G, Ferguson TB, Flegal K, Ford E, Furie K, Go A, Greenlund K, Haase N, Hailpern S, Ho M, Howard V, Kissela B, Kittner S, Lackland D, Lisabeth L, Marelli A, McDermott M, Meigs J, Mozaffarian D, Nichol G, O’Donnell C, Roger V, Rosamond W, Sacco R, Sorlie P, Stafford R, Steinberger J, Thom T, Wasserthiel-Smoller S, Wong N, Wylie-Rosett J, Hong Y American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics -- 2009 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2009;119:e21–e181. - PubMed
-
- Flynn KE, Piña IL, Whellan DJ, Lin L, Blumenthal JA, Ellis SJ, Fine LJ, Howlett JG, Keteyian SJ, Kitzman DW, Kraus WE, Miller NH, Schulman KA, Spertus JA, O’Connor CM, Weinfurt KP. Effects of exercise training on health status in patients with chronic heart failure: HF-ACTION randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2009;301:1451–1459. - PMC - PubMed
-
- O’Connor CM, Whellan DJ, Lee KL, Keteyian SJ, Cooper LS, Ellis SJ, Leifer ES, Kraus WE, Kitzman DW, Blumenthal JA, Rendall DS, Miller NH, Fleg JL, Schulman KA, McKelvie RS, Zannad F, Piña IL HF-ACTION Investigators. Efficacy and safety of exercise training in patients with chronic heart failure: HF-ACTION randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2009;301:1439–50. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- 5U01HL066461/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL064264/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL064250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG018915/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL064265/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066497/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL064264/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL066482/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL066497/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P60AG010484/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068980/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL064250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL064265/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066491/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL068973/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL064257/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37AG018915/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL064257/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066482/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL063747/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL066491/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066494/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL066501/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066461/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068973/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL068980/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL063747/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL066494/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066501/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

