FEN1 ensures telomere stability by facilitating replication fork re-initiation
- PMID: 20551483
- PMCID: PMC2930705
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.112276
FEN1 ensures telomere stability by facilitating replication fork re-initiation
Abstract
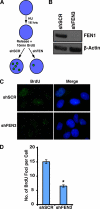
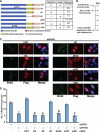
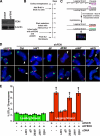
Telomeres are terminal repetitive DNA sequences whose stability requires the coordinated actions of telomere-binding proteins and the DNA replication and repair machinery. Recently, we demonstrated that the DNA replication and repair protein Flap endonuclease 1 (FEN1) is required for replication of lagging strand telomeres. Here, we demonstrate for the first time that FEN1 is required for efficient re-initiation of stalled replication forks. At the telomere, we find that FEN1 depletion results in replicative stress as evidenced by fragile telomere expression and sister telomere loss. We show that FEN1 participation in Okazaki fragment processing is not required for efficient telomere replication. Instead we find that FEN1 gap endonuclease activity, which processes DNA structures resembling stalled replication forks, and the FEN1 interaction with the RecQ helicases are vital for telomere stability. Finally, we find that FEN1 depletion neither impacts cell cycle progression nor in vitro DNA replication through non-telomeric sequences. Our finding that FEN1 is required for efficient replication fork re-initiation strongly suggests that the fragile telomere expression and sister telomere losses observed upon FEN1 depletion are the direct result of replication fork collapse. Together, these findings suggest that other nucleases compensate for FEN1 loss throughout the genome during DNA replication but fail to do so at the telomere. We propose that FEN1 maintains stable telomeres by facilitating replication through the G-rich lagging strand telomere, thereby ensuring high fidelity telomere replication.
Figures

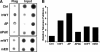
Similar articles
-
Flap Endonuclease 1 Limits Telomere Fragility on the Leading Strand.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jun 12;290(24):15133-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.647388. Epub 2015 Apr 28. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25922071 Free PMC article.
-
Flap endonuclease 1 contributes to telomere stability.Curr Biol. 2008 Apr 8;18(7):496-500. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.02.071. Curr Biol. 2008. PMID: 18394896 Free PMC article.
-
Human flap endonuclease I is in complex with telomerase and is required for telomerase-mediated telomere maintenance.J Biol Chem. 2009 Feb 6;284(6):3682-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M805362200. Epub 2008 Dec 9. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19068479 Free PMC article.
-
Flap endonuclease 1.Annu Rev Biochem. 2013;82:119-38. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-072511-122603. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Annu Rev Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23451868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Flap endonuclease-1 and its role in the processes of DNA metabolism in eucaryotic cells].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2008 May-Jun;42(3):405-21. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2008. PMID: 18702299 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Flap Endonuclease 1 Limits Telomere Fragility on the Leading Strand.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jun 12;290(24):15133-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.647388. Epub 2015 Apr 28. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25922071 Free PMC article.
-
Human CST promotes telomere duplex replication and general replication restart after fork stalling.EMBO J. 2012 Aug 29;31(17):3537-49. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.215. Epub 2012 Aug 3. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22863775 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Methylation of Telomere-Related Genes and Cancer Risk.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2018 Aug;11(8):511-522. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-17-0413. Epub 2018 Jun 12. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2018. PMID: 29895583 Free PMC article.
-
Condensin II interacts with BLM helicase in S phase to maintain genome stability.Commun Biol. 2025 Mar 25;8(1):492. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07916-0. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40133469 Free PMC article.
-
USP50 suppresses alternative RecQ helicase use and deleterious DNA2 activity during replication.Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 16;15(1):8102. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52250-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39284827 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

