Immunogenicity for CD8+ and CD4+ T cells of 2 formulations of an incomplete freund's adjuvant for multipeptide melanoma vaccines
- PMID: 20551833
- PMCID: PMC3218563
- DOI: 10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181e311ac
Immunogenicity for CD8+ and CD4+ T cells of 2 formulations of an incomplete freund's adjuvant for multipeptide melanoma vaccines
Abstract
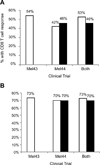
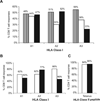
An incomplete Freund's adjuvant (IFA) commonly used in experimental cancer vaccines has recently been reformulated. Oleic acid used in the surfactant was purified from a vegetable source (olives, IFA-VG) rather than an animal source (beef tallow, IFA-AN). To provide an insight into the adjuvant properties of the new formulation, we reviewed T-cell responses, by enzyme-linked immunospot assay, to multipeptide vaccines in 2 sequential clinical trials that spanned this transition of adjuvants. Analyses included 194 patients who received either IFA-AN or IFA-VG for all vaccines, and a subset of 93 patients best matched by study arm for vaccine antigens (12 melanoma peptides restricted by major histocompatibility complex class I, 12MP; plus a tetanus helper peptide, tet) administered with IFA but without granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor. Inflammation was observed at vaccine sites clinically for almost all patients, even including ulceration in a subset with each IFA formulation. CD8 T-cell response rates to the 12 melanoma peptides were 53% [95% confidence interval (CI), 44%, 61%)] for IFA-AN and 46% [95% CI, 32%, 59%)] for IFA-VG. In the 93 patient subset, these rates were 73% [95% CI, 61%, 83%)] and 70% [95% CI, 47%, 87%)], respectively. CD4 T-cell responses to tetanus helper peptide were identified in 94% [95% CI, 86%, 98%)] and 96% [95% CI, 78%, 100%)], respectively. Responses to individual human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-A1, A2, and DR associated peptides were largely preserved, but reactivity trended lower for some HLA-A3 associated peptides. Despite the necessarily retrospective nature of the analysis and limitations of multiple comparisons, our summary data support the use of IFA-VG as an adjuvant with multipeptide vaccines in melanoma patients.
Conflict of interest statement
CLS is listed as an inventor for several peptides used in the melanoma vaccines used in the clinical trials reported in this manuscript, but those patents were filed by the University of Virginia Patent Foundation and have been licensed to Glaxo Smith Kline. All other authors have declared there are no financial conflicts of interest in regards to this work.
Figures
References
-
- Bonhoure F, Gaucheron J. Montanide ISA 51 VG as Adjuvant for Human Vaccines. Journal of Immunotherapy. 2006;29:647–648.
-
- Slingluff CL, Jr, Yamshchikov G, Neese P, et al. Phase I trial of a melanoma vaccine with gp100(280–288) peptide and tetanus helper peptide in adjuvant immunologic and clinical outcomes. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:3012–3024. - PubMed
-
- Chianese-Bullock KA, Pressley J, Garbee C, et al. MAGE-A1-, MAGE-A10-, and gp100-derived peptides are immunogenic when combined with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and montanide ISA-51 adjuvant and administered as part of a multipeptide vaccine for melanoma. JI. 2005;174:3080–3086. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

