Techniques to study specific cell-surface receptor-mediated cellular vitamin A uptake
- PMID: 20552439
- PMCID: PMC3907174
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-60327-325-1_20
Techniques to study specific cell-surface receptor-mediated cellular vitamin A uptake
Abstract
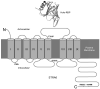
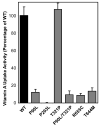
STRA6 is a multitransmembrane domain protein that was recently identified as the cell-surface receptor for plasma retinol-binding protein (RBP), the vitamin A carrier protein in the blood. STRA6 binds to RBP with high affinity and mediates cellular uptake of vitamin A from RBP. It is not homologous to any known receptors, transporters, and channels, and it represents a new class of membrane transport protein. Consistent with the diverse physiological functions of vitamin A, STRA6 is widely expressed in diverse adult organs and throughout embryonic development. Mutations in human STRA6 that abolish its vitamin A uptake activity cause severe pathological phenotypes in many human organs including the eye, brain, lung, and heart. This chapter describes functional assays for STRA6 in live cells and on cellular membranes. These assays can be employed to study the mechanism of this new membrane transport mechanism and its roles in the physiology and pathology of many organs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The membrane receptor for plasma retinol-binding protein, a new type of cell-surface receptor.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2011;288:1-41. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386041-5.00001-7. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21482409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A membrane receptor for retinol binding protein mediates cellular uptake of vitamin A.Science. 2007 Feb 9;315(5813):820-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1136244. Epub 2007 Jan 25. Science. 2007. PMID: 17255476
-
Regulatory mechanism for the transmembrane receptor that mediates bidirectional vitamin A transport.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 May 5;117(18):9857-9864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1918540117. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32300017 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the membrane topology and extracellular ligand binding domains of the retinol binding protein receptor.Biochemistry. 2008 May 13;47(19):5387-95. doi: 10.1021/bi8002082. Epub 2008 Apr 18. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18419130 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a membrane receptor for retinol-binding protein functioning in the cellular uptake of retinol.Nutr Rev. 2007 Aug;65(8 Pt 1):385-8. doi: 10.1301/nr.2007.aug.385-388. Nutr Rev. 2007. PMID: 17867372 Review.
Cited by
-
Vitamin A metabolism: an update.Nutrients. 2011 Jan;3(1):63-103. doi: 10.3390/nu3010063. Nutrients. 2011. PMID: 21350678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying candidate reference chemicals for in vitro testing of the retinoid pathway for predictive developmental toxicity.ALTEX. 2023;40(2):217–236. doi: 10.14573/altex.2202231. Epub 2022 Jun 23. ALTEX. 2023. PMID: 35796328 Free PMC article.
-
An in vitro model for vitamin A transport across the human blood-brain barrier.Elife. 2023 Nov 7;12:RP87863. doi: 10.7554/eLife.87863. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37934575 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping of the extracellular RBP4 ligand binding domain on the RBPR2 receptor for Vitamin A transport.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Feb 22;11:1105657. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1105657. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36910150 Free PMC article.
-
Retinol-binding protein 4 and its membrane receptor STRA6 control adipogenesis by regulating cellular retinoid homeostasis and retinoic acid receptor α activity.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Oct;33(20):4068-82. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00221-13. Epub 2013 Aug 19. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23959802 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blomhoff R. Overview of Vitamin A Metabolism and Function. In: Blomhoff R, editor. Vitamin A in Health and Disease. Marcel Dekker, Inc.; 1994. pp. 1–35.
-
- Ross AC, Gardner EM. The function of vitamin A in cellular growth and differentiation, and its roles during pregnancy and lactation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1994;352:187–200. - PubMed
-
- Napoli JL. Biochemical pathways of retinoid transport, metabolism, and signal transduction. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1996;80:S52–62. - PubMed
-
- Evans RM. The molecular basis of signaling by vitamin A and its metabolites. Harvey Lect. 1994;90:105–117. - PubMed
-
- Chambon P. A decade of molecular biology of retinoic acid receptors. FASEB J. 1996;10:940–954. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

