Communicating subcellular distributions
- PMID: 20552685
- PMCID: PMC2901539
- DOI: 10.1002/cyto.a.20933
Communicating subcellular distributions
Abstract
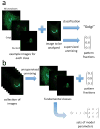
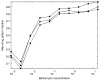
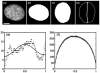
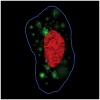
To build more accurate models of cells and tissues, the ability to incorporate information on the distributions of proteins (and other macromolecules) will become increasingly important. This review describes current progress towards determining and representing protein subcellular patterns so that the information can be used as part of systems biology efforts. Approaches to decomposing an image of the subcellular pattern of a protein give critical information about the fraction of that protein in each of a number of fundamental patterns (e.g., organelles). Methods for learning generative models from images provide a means of capturing the essential properties and variation in those properties of cell shape and organelle patterns. The combination of models of fundamental patterns and vectors specifying the fraction of a protein in each of them provide a much better means of communicating subcellular patterns than the descriptive terms that are currently used. Communicating information about subcellular patterns is important not only for systems biology simulations but also for representing results from microscopy experiments, including high content screening and imaging flow cytometry, in a transportable and generalizable manner.
Figures


References
-
- Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium Nat Genet. 2000;25(1):25–9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chou KC, Shen HB. Recent progress in protein subcellular location prediction. Anal Biochem. 2007;370(1):1–16. - PubMed
-
- Shatkay H, Hoglund A, Brady S, Blum T, Donnes P, Kohlbacher O. SherLoc: high-accuracy prediction of protein subcellular localization by integrating text and protein sequence data. Bioinformatics. 2007;23(11):1410–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

