Nonhistone protein acetylation as cancer therapy targets
- PMID: 20553216
- PMCID: PMC3273412
- DOI: 10.1586/era.10.62
Nonhistone protein acetylation as cancer therapy targets
Abstract
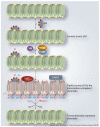
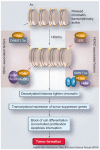
Acetylation and deacetylation are counteracting, post-translational modifications that affect a large number of histone and nonhistone proteins. The significance of histone acetylation in the modification of chromatin structure and dynamics, and thereby gene transcription regulation, has been well recognized. A steadily growing number of nonhistone proteins have been identified as acetylation targets and reversible lysine acetylation in these proteins plays an important role(s) in the regulation of mRNA stability, protein localization and degradation, and protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions. The recruitment of histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs) to the transcriptional machinery is a key element in the dynamic regulation of genes controlling cellular proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. Many nonhistone proteins targeted by acetylation are the products of oncogenes or tumor-suppressor genes and are directly involved in tumorigenesis, tumor progression and metastasis. Aberrant activity of HDACs has been documented in several types of cancers and HDAC inhibitors (HDACi) have been employed for therapeutic purposes. Here we review the published literature in this field and provide updated information on the regulation and function of nonhistone protein acetylation. While concentrating on the molecular mechanism and pathways involved in the addition and removal of the acetyl moiety, therapeutic modalities of HDACi are also discussed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deacetylation of nonhistone proteins by HDACs and the implications in cancer.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2011;206:39-56. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-21631-2_3. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21879445 Review.
-
Using Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors to Analyze the Relevance of HDACs for Translation.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1510:77-91. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6527-4_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27761814
-
HDACs and HDAC Inhibitors in Cancer Development and Therapy.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016 Oct 3;6(10):a026831. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a026831. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016. PMID: 27599530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation by the acetylation of nonhistone proteins in humans -- a new target for therapeutics.IUBMB Life. 2005 Mar;57(3):137-49. doi: 10.1080/15216540500090629. IUBMB Life. 2005. PMID: 16036576 Review.
-
Targeting the acetylation signaling pathway in cancer therapy.Semin Cancer Biol. 2022 Oct;85:209-218. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.03.001. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022. PMID: 33705871 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Review on Molecular Docking on HDAC Isoforms: Novel Tool for Designing Selective Inhibitors.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Nov 22;16(12):1639. doi: 10.3390/ph16121639. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38139766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A possible link to uracil DNA glycosylase in the synergistic action of HDAC inhibitors and thymidylate synthase inhibitors.J Transl Med. 2020 Oct 7;18(1):377. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02555-x. J Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 33028332 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis Induction byHistone Deacetylase Inhibitors in Cancer Cells: Role of Ku70.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 30;20(7):1601. doi: 10.3390/ijms20071601. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30935057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone deacetylase 6 controls Notch3 trafficking and degradation in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells.Oncogene. 2018 Jul;37(28):3839-3851. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0234-z. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29643474 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Protein Acetylation in Cells Using Heterobifunctional Molecules.J Am Chem Soc. 2021 Oct 13;143(40):16700-16708. doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c07850. Epub 2021 Sep 30. J Am Chem Soc. 2021. PMID: 34592107 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
Buchwald M, Kramer OH, Heinzel T. HDACi – targets beyond chromatin. Cancer Lett. 2009;280(2):160–167. •• Describes histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACi)-mediated depletion of oncoproteins via modulation of the abundance of enzymes of the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway. It highlights the cytokine- and HDACi-stimulated acetylation-dependent cross-talks of STAT/NF-κB signaling pathways. It also describes how the reagents could be beneficial for the treatment and prevention of human ailments, such as cancer and unbalanced immune functions.
-
-
-
Spange S, Wagner T, Heinzel T, Krämer OH. Acetylation of non-histone proteins modulates cellular signalling at multiple levels. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009;41(1):185–198. •• Detailed review of the post-translational acetylation of nonhistone proteins as well as the complex and dynamic nature of the cellular acetylome. Acetylation alterations are frequently involved in physiological and pathophysiological pathways.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
