Protein tandem repeats - the more perfect, the less structured
- PMID: 20553501
- PMCID: PMC2928880
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-464X.2010.07684.x
Protein tandem repeats - the more perfect, the less structured
Abstract
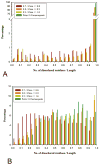
We analysed the structural properties of protein regions containing arrays of perfect and nearly perfect tandem repeats. Naturally occurring proteins with perfect repeats are practically absent among the proteins with known 3D structures. The great majority of such regions in the Protein Data Bank are found in the proteins designed de novo. The abundance of natural structured proteins with tandem repeats is inversely correlated with the repeat perfection: the chance of finding natural structured proteins in the Protein Data Bank increases with a decrease in the level of repeat perfection. Prediction of intrinsic disorder within the tandem repeats in the SwissProt proteins supports the conclusion that the level of repeat perfection correlates with their tendency to be unstructured. This correlation is valid across the various species and subcellular localizations, although the level of disordered tandem repeats varies significantly between these datasets. On average, in prokaryotes, tandem repeats of cytoplasmic proteins were predicted to be the most structured, whereas in eukaryotes, the most structured portion of the repeats was found in the membrane proteins. Our study supports the hypothesis that, in general, the repeat perfection is a sign of recent evolutionary events rather than of exceptional structural and (or) functional importance of the repeat residues.
Keywords: bioinformatics; disordered conformation; evolution; protein structure; sequence analysis.
Figures



References
-
- Pellegrini M, Marcotte EM, Yeates TO. A fast algorithm for genome-wide analysis of proteins with repeated sequences. Proteins. 1999;35:440–446. - PubMed
-
- Fraser RDB, MacRae TP. Conformation in fibrous proteins and related synthetic polypeptides. Academic Press; London and New York: 1973.
-
- Yoder MD, Lietzke SE, Jurnak F. Unusual structural features in the parallel beta-helix in pectate lyases. Structure. 1993;1:241–251. - PubMed
-
- Kobe B, Kajava AV. The leucine-rich repeat as a protein recognition motif. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2001;11:725–732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

