Undetected antisense tRNAs in mitochondrial genomes?
- PMID: 20553583
- PMCID: PMC2907346
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6150-5-39
Undetected antisense tRNAs in mitochondrial genomes?
Abstract
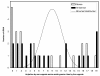
Background: The hypothesis that both mitochondrial (mt) complementary DNA strands of tRNA genes code for tRNAs (sense-antisense coding) is explored. This could explain why mt tRNA mutations are 6.5 times more frequently pathogenic than in other mt sequences. Antisense tRNA expression is plausible because tRNA punctuation signals mt sense RNA maturation: both sense and antisense tRNAs form secondary structures potentially signalling processing. Sense RNA maturation processes by default 11 antisense tRNAs neighbouring sense genes. If antisense tRNAs are expressed, processed antisense tRNAs should have adapted more for translational activity than unprocessed ones. Four tRNA properties are examined: antisense tRNA 5' and 3' end processing by sense RNA maturation and its accuracy, cloverleaf stability and misacylation potential.
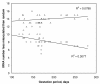
Results: Processed antisense tRNAs align better with standard tRNA sequences with the same cognate than unprocessed antisense tRNAs, suggesting less misacylations. Misacylation increases with cloverleaf fragility and processing inaccuracy. Cloverleaf fragility, misacylation and processing accuracy of antisense tRNAs decrease with genome-wide usage of their predicted cognate amino acid.
Conclusions: These properties correlate as if they adaptively coevolved for translational activity by some antisense tRNAs, and to avoid such activity by other antisense tRNAs. Analyses also suggest previously unsuspected particularities of aminoacylation specificity in mt tRNAs: combinations of competition between tRNAs on tRNA synthetases with competition between tRNA synthetases on tRNAs determine specificities of tRNA amino acylations. The latter analyses show that alignment methods used to detect tRNA cognates yield relatively robust results, even when they apparently fail to detect the tRNA's cognate amino acid and indicate high misacylation potential.
Figures






References
-
- Seligmann H, Pollock DD. Function and evolution of secondary structure in human mitochondrial mRNAs. Midsouth Computational Biology and Bioinformatics Society. 2003. Abstract 26.
-
- Krishnan NM, Seligmann H, Raina SZ, Pollock DD. In: Curr in Comput Mol Biol. Gramada A, Bourna PE, editor. 2004. Phylogenetic analysis of site-specific perturbations ina symmetric mutation gradients; pp. 266–267.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

