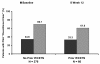Effectiveness and safety of adalimumab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis or psoriatic arthritis and history of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy
- PMID: 20553600
- PMCID: PMC2911911
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3054
Effectiveness and safety of adalimumab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis or psoriatic arthritis and history of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy
Abstract
Introduction: Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) antagonists reduce the signs and symptoms of spondyloarthritides, including ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Our objective was to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of adalimumab, 40 mg every other week, for patients with AS or PsA and prior treatment with infliximab (IFX) and/or etanercept (ETN).
Methods: Both trials were 12-week, open-label studies with an optional extension period up to week 20. Patients were stratified by history of anti-TNF treatment, prior anti-TNF therapy received (IFX, ETN, or both), and reason for discontinuation of prior TNF antagonist. ETN was discontinued>or=3 weeks, and IFX was discontinued>or=2 months before the first adalimumab administration. Effectiveness at week 12 was evaluated by using observed standard-outcome measurements for AS and PsA.
Results: At week 12 of adalimumab treatment, Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index 50 responses were achieved by 40.8% of 326 patients with AS who had received prior anti-TNF therapy and by 63.0% of 924 patients with AS who were naive to TNF antagonist. Observed response rates were generally greater for patients who discontinued the prior anti-TNF therapy because of loss of response or intolerance than for patients who discontinued because of lack of response. Median changes in swollen-joint count and in enthesitis score were similar in patients with and without prior TNF-antagonist treatment. Modified PsA response criteria were fulfilled by 71.2% of 66 patients with PsA, with prior exposure to TNF antagonists, and by 78.8% of 376 patients with no history of anti-TNF therapy. The percentages of patients with PsA attaining a Physician's Global Assessment of psoriasis of "Clear/Almost clear" increased from 33.3% to 61.0% for patients with prior IFX and/or ETN treatment and from 34.6% to 69.7% for patients without anti-TNF therapy. The median change in the Nail Psoriasis Severity Index was -6 for both groups. In both studies, patterns of adverse events were similar for patients with and without prior anti-TNF therapy and were consistent with the known safety profile of adalimumab.
Conclusions: Patients with AS or PsA previously treated with IFX and/or ETN experienced clinically relevant improvements of their diseases after 12 weeks of adalimumab.
Trial registrations: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00478660 and NCT00235885.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Costs of tumor necrosis factor blockers per treated patient using real-world drug data in a managed care population.J Manag Care Pharm. 2013 Oct;19(8):621-30. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2013.19.8.621. J Manag Care Pharm. 2013. PMID: 24074008 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of effectiveness and safety of infliximab, etanercept, and adalimumab in psoriatic arthritis patients who experienced an inadequate response to previous disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs.Clin Rheumatol. 2010 Apr;29(4):399-403. doi: 10.1007/s10067-009-1340-7. Clin Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 20066450 Clinical Trial.
-
Switching tumour necrosis factor alpha antagonists in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis: an observational study over a 5-year period.Ann Rheum Dis. 2007 Oct;66(10):1393-7. doi: 10.1136/ard.2007.073569. Epub 2007 Jul 5. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007. PMID: 17613555 Free PMC article.
-
TNF alpha inhibitors in the treatment of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.BioDrugs. 2005;19(1):47-57. doi: 10.2165/00063030-200519010-00006. BioDrugs. 2005. PMID: 15691217 Review.
-
[Anti-TNF alpha in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis].Presse Med. 2006 Apr;35(4 Pt 2):647-55. doi: 10.1016/s0755-4982(06)74658-9. Presse Med. 2006. PMID: 16614610 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Nail Psoriasis: A Review of Treatment Options.Drugs. 2016 Apr;76(6):675-705. doi: 10.1007/s40265-016-0564-5. Drugs. 2016. PMID: 27041288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring sub-optimal response to tumour necrosis factor inhibitors in axial spondyloarthritis.Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2019 May 4;3(1):rkz012. doi: 10.1093/rap/rkz012. eCollection 2019. Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2019. PMID: 31432000 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of upadacitinib in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis refractory to biologic therapy: 2-year clinical and radiographic results from the open-label extension of the SELECT-AXIS 2 study.Arthritis Res Ther. 2024 Nov 12;26(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03412-8. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39533349 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Long-Term Safety of Adalimumab in 29,967 Adult Patients From Global Clinical Trials Across Multiple Indications: An Updated Analysis.Adv Ther. 2020 Jan;37(1):364-380. doi: 10.1007/s12325-019-01145-8. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Adv Ther. 2020. PMID: 31748904 Free PMC article.
-
Korean treatment recommendations for patients with axial spondyloarthritis.J Rheum Dis. 2023 Jul 1;30(3):151-169. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2023.0025. J Rheum Dis. 2023. PMID: 37476674 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Furst DE, Keystone EC, Fleischmann R, Mease P, Breedveld FC, Smolen JS, Kalden JR, Braun J, Bresnihan B, Burmester GR, De Benedetti F, Dörner T, Emery P, Gibofsky A, Kavanaugh A, Kirkham B, Schiff MH, Sieper J, Singer N, Van Riel PL, Weinblatt ME, Weisman MH, Winthrop K. Updated consensus statement on biological agents for the treatment of rheumatic diseases, 2009. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;69 Suppl 1:i2–i29. doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.123885. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Conti F, Ceccarelli F, Marocchi E, Magrini L, Spinelli FR, Spadaro A, Scrivo R, Valesini G. Switching tumour necrosis factor alpha antagonists in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis: an observational study over a 5-year period. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66:1393–1397. doi: 10.1136/ard.2007.073569. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bombardieri S, Ruiz AA, Fardellone P, Geusens P, McKenna F, Unnebrink K, Oezer U, Kary S, Kupper H, Burmester GR. Effectiveness of adalimumab for rheumatoid arthritis in patients with a history of TNF-antagonist therapy in clinical practice. Rheumatology. 2007;46:1191–1199. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kem091. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous