Comparative transcriptional profiling-based identification of raphanusanin-inducible genes
- PMID: 20553608
- PMCID: PMC3095276
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-111
Comparative transcriptional profiling-based identification of raphanusanin-inducible genes
Abstract
Background: Raphanusanin (Ra) is a light-induced growth inhibitor involved in the inhibition of hypocotyl growth in response to unilateral blue-light illumination in radish seedlings. Knowledge of the roles of Ra still remains elusive. To understand the roles of Ra and its functional coupling to light signalling, we constructed the Ra-induced gene library using the Suppression Subtractive Hybridisation (SSH) technique and present a comparative investigation of gene regulation in radish seedlings in response to short-term Ra and blue-light exposure.
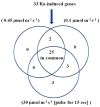
Results: The predicted gene ontology (GO) term revealed that 55% of the clones in the Ra-induced gene library were associated with genes involved in common defence mechanisms, including thirty four genes homologous to Arabidopsis genes implicated in R-gene-triggered resistance in the programmed cell death (PCD) pathway. Overall, the library was enriched with transporters, hydrolases, protein kinases, and signal transducers. The transcriptome analysis revealed that, among the fifty genes from various functional categories selected from 88 independent genes of the Ra-induced library, 44 genes were up-regulated and 4 were down-regulated. The comparative analysis showed that, among the transcriptional profiles of 33 highly Ra-inducible genes, 25 ESTs were commonly regulated by different intensities and duration of blue-light irradiation. The transcriptional profiles, coupled with the transcriptional regulation of early blue light, have provided the functional roles of many genes expected to be involved in the light-mediated defence mechanism.
Conclusions: This study is the first comprehensive survey of transcriptional regulation in response to Ra. The results described herein suggest a link between Ra and cellular defence and light signalling, and thereby contribute to further our understanding of how Ra is involved in light-mediated mechanisms of plant defence.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Raphanusanin-mediated resistance to pathogens is light dependent in radish and Arabidopsis thaliana.Planta. 2014 Sep;240(3):513-24. doi: 10.1007/s00425-014-2103-5. Epub 2014 Jun 13. Planta. 2014. PMID: 24923677
-
Raphanusanin-induced genes and the characterization of RsCSN3, a raphanusanin-induced gene in etiolated radish hypocotyls.Phytochemistry. 2008 Nov;69(16):2781-92. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2008.09.014. Epub 2008 Oct 24. Phytochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18952246
-
Spatial Regulation of the Gene Expression Response to Shade in Arabidopsis Seedlings.Plant Cell Physiol. 2015 Jul;56(7):1306-19. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcv057. Epub 2015 Apr 22. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25907567
-
Chromium stress mitigation by polyamine-brassinosteroid application involves phytohormonal and physiological strategies in Raphanus sativus L.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33210. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033210. Epub 2012 Mar 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22479371 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid, organ-specific transcriptional responses to light regulate photomorphogenic development in dicot seedlings.Plant Physiol. 2011 Aug;156(4):2124-40. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.179416. Epub 2011 Jun 7. Plant Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21653191 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Raphanusanin-mediated resistance to pathogens is light dependent in radish and Arabidopsis thaliana.Planta. 2014 Sep;240(3):513-24. doi: 10.1007/s00425-014-2103-5. Epub 2014 Jun 13. Planta. 2014. PMID: 24923677
References
-
- Kosemura S, Yamamura S, Hasegawa K. Chemical studies on 4-Methylthio-3-butenyl isothiocyanate from roots of japanese radish (Raphanus sativus L.) in connection with raphanusanins, phototropism-regulating substances of radish hypotyls. Tetrahedron Letts. 1993;34:481–484. doi: 10.1016/0040-4039(93)85107-8. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

