Expression of the zic1, zic2, zic3, and zic4 genes in early chick embryos
- PMID: 20553611
- PMCID: PMC2908108
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-3-167
Expression of the zic1, zic2, zic3, and zic4 genes in early chick embryos
Abstract
Background: The zic genes encode a family of transcription factors with important roles during early development. Since little is known about zic gene expression in chick embryos, we have characterized the expression patterns of the zic1, zic2, zic3, and zic4 (zic1-4) genes during neurulation and somitogenesis.
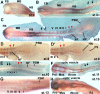
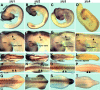
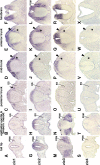
Findings: We used in situ hybridization to analyze the expression patterns of the zic1-4 genes during early chick development (HH stages 7-19). The zic1-3 genes showed both overlapping and gene-specific expression patterns along the length of the dorsal neural tube and in the dorsal parts of the somites. In addition, unique expression domains of zic genes included: zic2 in the neural plate, periotic mesoderm and limb buds; zic3 in the paraxial mesoderm surrounding the neural plate, in presomitic mesoderm and in the most recently formed epithelial somites; zic2 and zic3 in developing eyes. zic4 expression was limited to dorsal fore- and midbrain regions and, unlike the expression of the zic1-3 genes, zic4 expression was not detected in the hindbrain and trunk. This was in contrast to more extensive zic4 expression in other vertebrates.
Conclusions: The zic1-3 genes were expressed in both overlapping and unique domains within the neural tube, somites and other ectoderm and mesoderm-derived structures in the future head and trunk. zic4 expression, however, was limited to dorso-anterior regions of the future brain. This is the first comprehensive study of zic1-4 gene expression in chick embryos during neurulation and somitogenesis.
Figures


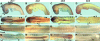
Similar articles
-
Expression of ZIC genes in the development of the chick inner ear and nervous system.Dev Dyn. 2003 Apr;226(4):702-12. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.10262. Dev Dyn. 2003. PMID: 12666207
-
The expression of the mouse Zic1, Zic2, and Zic3 gene suggests an essential role for Zic genes in body pattern formation.Dev Biol. 1997 Feb 15;182(2):299-313. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1996.8449. Dev Biol. 1997. PMID: 9070329
-
Zic2 and Zic3 synergistically control neurulation and segmentation of paraxial mesoderm in mouse embryo.Dev Biol. 2007 Jun 15;306(2):669-84. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.04.003. Epub 2007 Apr 12. Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17490632
-
Zic Genes in Teleosts: Their Roles in Dorsoventral Patterning in the Somite.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1046:141-156. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-7311-3_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29442321 Review.
-
Zic Family Proteins in Emerging Biomedical Studies.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1046:233-248. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-7311-3_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29442325 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of the WNT/β-catenin pathway in central nervous system primitive neuroectodermal tumours (CNS PNETs).Br J Cancer. 2013 May 28;108(10):2130-41. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.170. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Br J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23591193 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into neural lineages via an early intermediate ectoderm population.Stem Cells. 2020 Nov;38(11):1400-1408. doi: 10.1002/stem.3260. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Stem Cells. 2020. PMID: 32745311 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of GLI3-ZIC3 interaction in the cadmium-induced omphalocele chick model.Pediatr Surg Int. 2011 Feb;27(2):205-9. doi: 10.1007/s00383-010-2779-y. Pediatr Surg Int. 2011. PMID: 21069353
-
Transcriptomic analysis of avian digits reveals conserved and derived digit identities in birds.Nature. 2011 Sep 4;477(7366):583-6. doi: 10.1038/nature10391. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21892187
-
Genetics Underlying the Interactions between Neural Crest Cells and Eye Development.J Dev Biol. 2020 Nov 10;8(4):26. doi: 10.3390/jdb8040026. J Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33182738 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kuo JS, Patel M, Gamse J, Merzdorf C, Liu X, Apekin V, Sive H. Opl: a zinc finger protein that regulates neural determination and patterning in Xenopus. Development. 1998;125:2867–82. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

