Conceptualizing the role of estrogens and serotonin in the development and maintenance of bulimia nervosa
- PMID: 20554102
- PMCID: PMC2910148
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cpr.2010.04.011
Conceptualizing the role of estrogens and serotonin in the development and maintenance of bulimia nervosa
Abstract
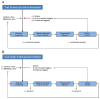
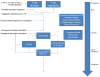
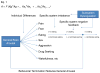
Serotonergic dysregulation is thought to underlie much of the pathology in bulimia nervosa (BN). The purpose of this review is to expand the serotonergic model by incorporating specific and nonspecific contributions of estrogens to the development and maintenance of bulimic pathology in order to guide research from molecular genetics to novel therapeutics for BN. Special emphasis is given to the organizing theory of general brain arousal which allows for integration of specific and nonspecific effects of these systems on behavioral endpoints such as binge eating or purging as well as arousal states such as fear, novelty seeking, or sex. Regulation of the serotonergic system by estrogens is explored, and genetic, epigenetic, and environmental estrogen effects on bulimic pathology and risk factors are discussed. Genetic and neuroscientific research support this two-system conceptualization of BN with both contributions to the developmental and maintenance of the disorder. Implications of an estrogenic-serotonergic model of BN are discussed as well as guidelines and suggestions for future research and novel therapeutic targets.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
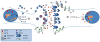
References
-
- Akimova E, Lanzenberger R, Kasper S. The serotonin-1A receptor in anxiety disorders. Biological Psychiatry. 2009;66(7):627–635. - PubMed
-
- Allen KL, Byrne SM, Forbes D, Oddy WH. Risk factors for full- and partial-syndrome early adolescent eating disorders: a population-based pregnancy cohort study. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 2009;48(8):800–809. - PubMed
-
- Amargos-Bosch M, Bortolozzi A, Puig MV, Serrats J, Adell A, Celada P, et al. Co-expression and in vivo interaction of serotonin(1A) and serotonin(2A) receptors in pyramidal neurons of prefrontal cortex. Cerebral Cortex. 2004;14(3):281–299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

