Overshooting dynamics in a model adaptive radiation
- PMID: 20554549
- PMCID: PMC3013401
- DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2010.0640
Overshooting dynamics in a model adaptive radiation
Abstract
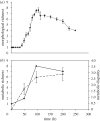
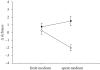
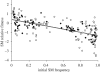
The history of life is punctuated by repeated periods of unusually rapid evolutionary diversification called adaptive radiation. The dynamics of diversity during a radiation reflect an overshooting pattern with an initial phase of exponential-like increase followed by a slower decline. Much attention has been paid to the factors that drive the increase phase, but far less is known about the causes of the decline phase. Decreases in diversity are rarely associated with climatic changes or catastrophic events, suggesting that they may be an intrinsic consequence of diversification. We experimentally identify the factors responsible for losses in diversity during the later stages of the model adaptive radiation of the bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens. Proximately, diversity declines because of the loss of biofilm-forming niche specialist morphotypes. We show that this loss occurs despite the presence of strong divergent selection late in the radiation and is associated with continued adaptation of resident niche specialists to both the biotic and abiotic environments. These results suggest that losses of diversity in the latter stages of an adaptive radiation may be a general consequence of diversification through competition and lends support to the idea that the conditions favouring the emergence of diversity are different from those that ensure its long-term maintenance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Competition both drives and impedes diversification in a model adaptive radiation.Proc Biol Sci. 2013 Sep 7;280(1766):20131253. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2013.1253. Print 2013 Sep 7. Proc Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23843392 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive radiation in a heterogeneous environment.Nature. 1998 Jul 2;394(6688):69-72. doi: 10.1038/27900. Nature. 1998. PMID: 9665128
-
Immigration history controls diversification in experimental adaptive radiation.Nature. 2007 Mar 22;446(7134):436-9. doi: 10.1038/nature05629. Nature. 2007. PMID: 17377582
-
Toward a general theory of adaptive radiation: insights from microbial experimental evolution.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009 Jun;1168:3-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04574.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009. PMID: 19566701 Review.
-
Adaptive radiation of Pseudomonas fluorescens SBW25 in experimental microcosms provides an understanding of the evolutionary ecology and molecular biology of A-L interface biofilm formation.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2017 Jul 3;364(12). doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnx109. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28535292 Review.
Cited by
-
Phylogenetic context determines the role of competition in adaptive radiation.Proc Biol Sci. 2016 Jun 29;283(1833):20160241. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2016.0241. Proc Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27335414 Free PMC article.
-
Enemy dispersal drives the diversity loss of bacterial victim populations at diversity cold spots.Evol Lett. 2025 Feb 22;9(3):346-354. doi: 10.1093/evlett/qraf004. eCollection 2025 Jun. Evol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40487869 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial storage effect promotes biodiversity during adaptive radiation.Proc Biol Sci. 2017 Jul 12;284(1858):20170841. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2017.0841. Proc Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28701564 Free PMC article.
-
Competition both drives and impedes diversification in a model adaptive radiation.Proc Biol Sci. 2013 Sep 7;280(1766):20131253. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2013.1253. Print 2013 Sep 7. Proc Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23843392 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial community structure of three traditional zambian fermented products: mabisi, chibwantu and munkoyo.PLoS One. 2013 May 14;8(5):e63948. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063948. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23691123 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Simpson G. G. 1953. The major features of evolution. New York, NY: Columbia University Press
-
- Gould S. J. 1989. Wonderful life: the burgess shale and the nature of history. London, UK: Penguin
-
- Benton M. J. 1996. Diversification and extinction in the history of life. Science 268, 52–5810.1126/science.7701342 (doi:10.1126/science.7701342) - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hedges S. B., Parker P. H., Sibley C. G., Kumar S. 1996. Continental breakup and the ordinal diversification of birds and mammals. Nature 381, 226–22910.1038/381226a0 (doi:10.1038/381226a0) - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gould S. J. 1987. Time's arrow, time's cycle: myth and metaphor in the discovery of geological time. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

