Toll-like receptor 2 mediates inhibition of HCO(3)(-) absorption by bacterial lipoprotein in medullary thick ascending limb
- PMID: 20554644
- PMCID: PMC2944297
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00108.2010
Toll-like receptor 2 mediates inhibition of HCO(3)(-) absorption by bacterial lipoprotein in medullary thick ascending limb
Abstract
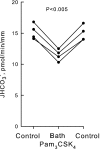
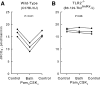
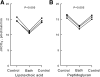
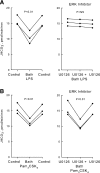
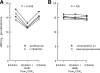
Bacterial infection and sepsis are associated with renal tubule dysfunction and dysregulation of systemic electrolyte balance but the underlying mechanisms are incompletely understood. Recently, we demonstrated that HCO(3)(-) absorption by the medullary thick ascending limb (MTAL) is inhibited by gram-negative bacterial LPS through activation of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). Here, we examined whether MTAL transport is altered by activation of TLR2, the receptor predominantly responsible for recognizing gram-positive bacteria. Confocal immunofluorescence showed expression of TLR2 in the basolateral membrane domain of rat and mouse MTALs. The functional role of TLR2 was examined in perfused MTALs using Pam(3)CSK(4), a bacterial lipoprotein analog that specifically activates TLR2. Adding Pam(3)CSK(4) to the bath decreased HCO(3)(-) absorption by 25%. The inhibition by Pam(3)CSK(4) was eliminated in MTALs from TLR2(-/-) mice. HCO(3)(-) absorption was also inhibited by the TLR2 agonists lipoteichoic acid and peptidoglycan, two cell wall components of gram-positive bacteria. The MEK/ERK inhibitor U0126 eliminated inhibition of HCO(3)(-) absorption by bath LPS but had no effect on inhibition by Pam(3)CSK(4). The inhibition by Pam(3)CSK(4) was eliminated by the protein kinase C inhibitors chelerythrine Cl and bisindolylmaleimide. Moreover, the inhibition by Pam(3)CSK(4), lipoteichoic acid, and peptidoglycan was additive to inhibition by LPS. Thus, agonists of basolateral TLR2 and TLR4 inhibit HCO(3)(-) absorption independently through distinct signaling pathways. We conclude that bacterial components act directly through TLRs to modify the transport function of renal tubules. During polymicrobial sepsis, gram-positive bacterial molecules acting through TLR2 and gram-negative LPS acting through TLR4 can function through parallel signaling pathways to impair MTAL transport. The inhibition of luminal acidification may impair the ability of the kidneys to correct systemic acidosis that contributes to sepsis pathogenesis.
Figures

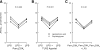
References
-
- Ahn KO, Lim SW, Yang HJ, Ghee JY, Kim JY, Kim SH, Kim J, Yang CW. Influence of angiotensin II on expression of Toll-like receptor 2 and maturation of dendritic cells in chronic cyclosporine nephropathy. Transplantation 83: 938–947, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124: 783–801, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Alberti C, Brun-Buisson C, Burchardi H, Martin C, Goodman S, Artigas A, Sicignano A, Palazzo M, Moreno R, Boulme R, Lepage E, Le Gall JR. Epidemiology of sepsis and infection in ICU patients from an international multicentre cohort study. Intensive Care Med 28: 108–121, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Alexopoulou L, Thomas V, Schnare M, Lobet Y, Anguita J, Schoen RT, Medzhitov R, Fikrig E, Flavell RA. Hyporesponsiveness to vaccination with borrelia burgdorferi OspA in humans and in TLR1- and TLR2-deficient mice. Nat Med 8: 878–884, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Aliprantis AO, Yang RB, Mark MR, Suggett S, Devaux B, Radolf JD, Klimpel GR, Godowski P, Zychlinsky A. Cell activation and apoptosis by bacterial lipoproteins through Toll-like receptor 2. Science 285: 736–739, 1999 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

