Purified mouse CYP27B1 can hydroxylate 20,23-dihydroxyvitamin D3, producing 1alpha,20,23-trihydroxyvitamin D3, which has altered biological activity
- PMID: 20554701
- PMCID: PMC2939470
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.110.034389
Purified mouse CYP27B1 can hydroxylate 20,23-dihydroxyvitamin D3, producing 1alpha,20,23-trihydroxyvitamin D3, which has altered biological activity
Abstract
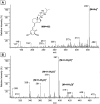
20,23-Dihydroxyvitamin D(3) [20,23(OH)(2)D(3)] is a biologically active metabolite produced by the action of cytochrome P450scc (CYP11A1) on vitamin D(3). It inhibits keratinocyte proliferation, stimulates differentiation, and inhibits nuclear factor-kappaB activity, working as a vitamin D receptor agonist. We have tested the ability of purified mouse 25-hydroxyvitamin D(3) 1alpha-hydroxylase (CYP27B1) to add a 1alpha-hydroxyl group to this vitamin D analog and determined whether this altered its biological activity. 20,23(OH)(2)D(3) incorporated into phospholipid vesicles was converted to a single product by CYP27B1, confirmed to be 1alpha,20,23-trihydroxyvitamin D(3) [1,20,23(OH)(3)D(3)] by mass spectrometry and NMR. The 20,23(OH)(2)D(3) was a relatively poor substrate for CYP27B1 compared with the normal substrate, 25-hydroxyvitamin D(3), displaying a 5-fold higher K(m) and 8-fold lower k(cat) value. Both 20,23(OH)(2)D(3) and 1,20,23(OH)(3)D(3) decreased neonatal human epidermal keratinocyte proliferation, showing significant effects at a lower concentration (0.1 nM) than that seen for 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) [1,25(OH)(2)D(3)] at 24 h of treatment. Both compounds also decreased cell biomass relative to that of control cells, measured by staining with sulforhodamine B. They caused little stimulation of the expression of the vitamin D receptor at the mRNA level compared with the 30-fold induction observed with the same concentration (100 nM) of 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) at 24 h. Addition of a 1alpha-hydroxyl group to 20,23(OH)(2)D(3) greatly enhanced its ability to stimulate the expression of the CYP24 gene but not to the extent seen with 1,25(OH)(2)D(3). This study shows that purified CYP27B1 can add a 1alpha-hydroxyl group to 20,23(OH)(2)D(3) with the product showing altered biological activity, especially for the stimulation of CYP24 gene expression.
Figures


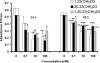



Similar articles
-
Hydroxylation of CYP11A1-derived products of vitamin D3 metabolism by human and mouse CYP27B1.Drug Metab Dispos. 2013 May;41(5):1112-24. doi: 10.1124/dmd.113.050955. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Drug Metab Dispos. 2013. PMID: 23454830 Free PMC article.
-
Production of 22-hydroxy metabolites of vitamin d3 by cytochrome p450scc (CYP11A1) and analysis of their biological activities on skin cells.Drug Metab Dispos. 2011 Sep;39(9):1577-88. doi: 10.1124/dmd.111.040071. Epub 2011 Jun 15. Drug Metab Dispos. 2011. PMID: 21677063 Free PMC article.
-
Potent antiproliferative effects of 25-hydroxy-16-ene-23-yne-vitamin D₃ that resists the catalytic activity of both CYP27B1 and CYP24A1.J Cell Biochem. 2014 Aug;115(8):1392-402. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24789. J Cell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24535953
-
Metabolism of vitamin D3 by cytochromes P450.Front Biosci. 2005 Jan 1;10:119-34. doi: 10.2741/1514. Print 2005 Jan 1. Front Biosci. 2005. PMID: 15574355 Review.
-
Enzymatic studies on the key enzymes of vitamin D metabolism; 1 alpha-hydroxylase (CYP27B1) and 24-hydroxylase (CYP24).Biotechnol Annu Rev. 2001;7:179-94. doi: 10.1016/s1387-2656(01)07037-5. Biotechnol Annu Rev. 2001. PMID: 11686044 Review.
Cited by
-
Endogenously produced nonclassical vitamin D hydroxy-metabolites act as "biased" agonists on VDR and inverse agonists on RORα and RORγ.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 Oct;173:42-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.09.024. Epub 2016 Sep 28. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27693422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of 20S-hydroxyvitamin D3 analogs and their 1α-OH derivatives as potent vitamin D receptor agonists with anti-inflammatory activities.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 24;8(1):1478. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19183-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29367669 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo evidence for a novel pathway of vitamin D₃ metabolism initiated by P450scc and modified by CYP27B1.FASEB J. 2012 Sep;26(9):3901-15. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-208975. Epub 2012 Jun 8. FASEB J. 2012. PMID: 22683847 Free PMC article.
-
Antifibrogenic Activities of CYP11A1-derived Vitamin D3-hydroxyderivatives Are Dependent on RORγ.Endocrinology. 2021 Jan 1;162(1):bqaa198. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqaa198. Endocrinology. 2021. PMID: 33107570 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo production of novel vitamin D2 hydroxy-derivatives by human placentas, epidermal keratinocytes, Caco-2 colon cells and the adrenal gland.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014 Mar 5;383(1-2):181-92. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.12.012. Epub 2013 Dec 29. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24382416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson PH, Hendrix I, Sawyer RK, Zarrinkalam R, Manavis J, Sarvestani GT, May BK, Morris HA. (2008) Co-expression of CYP27B1 enzyme with the 1.5 kb CYP27B1 promoter-luciferase transgene in the mouse. Mol Cell Endocrinol 285:1–9 - PubMed
-
- Bouillon R, Eelen G, Verlinden L, Mathieu C, Carmeliet G, Verstuyf A. (2006) Vitamin D and cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 102:156–162 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

