Coxsackievirus B3 infection activates the unfolded protein response and induces apoptosis through downregulation of p58IPK and activation of CHOP and SREBP1
- PMID: 20554776
- PMCID: PMC2918999
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01416-09
Coxsackievirus B3 infection activates the unfolded protein response and induces apoptosis through downregulation of p58IPK and activation of CHOP and SREBP1
Abstract
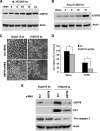
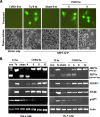
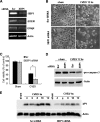
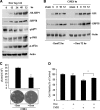
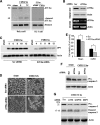
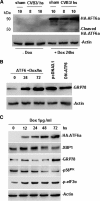
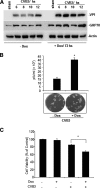
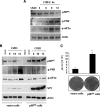
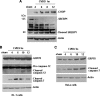
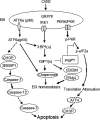
Cardiomyocyte apoptosis is a hallmark of coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3)-induced myocarditis. We used cardiomyocytes and HeLa cells to explore the cellular response to CVB3 infection, with a focus on pathways leading to apoptosis. CVB3 infection triggered endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and differentially regulated the three arms of the unfolded protein response (UPR) initiated by the proximal ER stress sensors ATF6a (activating transcription factor 6a), IRE1-XBP1 (X box binding protein 1), and PERK (PKR-like ER protein kinase). Upon CVB3 infection, glucose-regulated protein 78 expression was upregulated, and in turn ATF6a and XBP1 were activated via protein cleavage and mRNA splicing, respectively. UPR activity was further confirmed by the enhanced expression of UPR target genes ERdj4 and EDEM1. Surprisingly, another UPR-associated gene, p58(IPK), which often is upregulated during infections with other types of viruses, was downregulated at both mRNA and protein levels after CVB3 infection. These findings were observed similarly for uninfected Tet-On HeLa cells induced to overexpress ATF6a or XBP1. In exploring potential connections between the three UPR pathways, we found that the ATF6a-induced downregulation of p58(IPK) was associated with the activation of PKR (PERK) and the phosphorylation of eIF2alpha, suggesting that p58(IPK), a negative regulator of PERK and PKR, mediates cross-talk between the ATF6a/IRE1-XBP1 and PERK arms. Finally, we found that CVB3 infection eventually produced the induction of the proapoptoic transcription factor CHOP and the activation of SREBP1 and caspase-12. Taken together, these data suggest that CVB3 infection activates UPR pathways and induces ER stress-mediated apoptosis through the suppression of P58(IPK) and induction/activation of CHOP, SREBP1, and caspase-12.
Figures
References
-
- Abbate, A., G. Sinagra, R. Bussani, N. N. Hoke, M. Merlo, A. Varma, S. Toldo, F. N. Salloum, G. G. Biondi-Zoccai, G. W. Vetrovec, F. Crea, F. Silvestri, and A. Baldi. 2009. Apoptosis in patients with acute myocarditis. Am. J. Cardiol. 104:995-1000. - PubMed
-
- Andréoletti, L., D. Hober, P. Becquart, S. Belaich, M. C. Copin, V. Lambert, and P. Wattre. 1997. Experimental CVB3-induced chronic myocarditis in two murine strains: evidence of interrelationships between virus replication and myocardial damage in persistent cardiac infection. J. Med. Virol. 52:206-214. - PubMed
-
- Benali-Furet, N. L., M. Chami, L. Houel, F. De Giorgi, F. Vernejoul, D. Lagorce, L. Buscail, R. Bartenschlager, F. Ichas, R. Rizzuto, and P. Paterlini-Brechot. 2005. Hepatitis C virus core triggers apoptosis in liver cells by inducing ER stress and ER calcium depletion. Oncogene 24:4921-4933. - PubMed
-
- Boyce, M., and J. Yuan. 2006. Cellular response to endoplasmic reticulum stress: a matter of life or death. Cell Death Differ. 13:363-373. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

