Interaction of alphaVbeta3 and alphaVbeta6 integrins with human parechovirus 1
- PMID: 20554778
- PMCID: PMC2919010
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02176-09
Interaction of alphaVbeta3 and alphaVbeta6 integrins with human parechovirus 1
Abstract
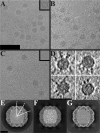
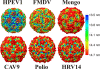
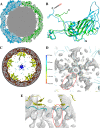
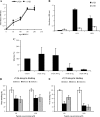
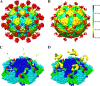
Human parechovirus (HPEV) infections are very common in early childhood and can be severe in neonates. It has been shown that integrins are important for cellular infectivity of HPEV1 through experiments using peptide blocking assays and function-blocking antibodies to alpha(V) integrins. The interaction of HPEV1 with alpha(V) integrins is presumably mediated by a C-terminal RGD motif in the capsid protein VP1. We characterized the binding of integrins alpha(V)beta(3) and alpha(V)beta(6) to HPEV1 by biochemical and structural studies. We showed that although HPEV1 bound efficiently to immobilized integrins, alpha(V)beta(6) bound more efficiently than alpha(V)beta(3) to immobilized HPEV1. Moreover, soluble alpha(V)beta(6), but not alpha(V)beta(3), blocked HPEV1 cellular infectivity, indicating that it is a high-affinity receptor for HPEV1. We also showed that HPEV1 binding to integrins in vitro could be partially blocked by RGD peptides. Using electron cryo-microscopy and image reconstruction, we showed that HPEV1 has the typical T=1 (pseudo T=3) organization of a picornavirus. Complexes of HPEV1 and integrins indicated that both integrin footprints reside between the 5-fold and 3-fold symmetry axes. This result does not match the RGD position predicted from the coxsackievirus A9 X-ray structure but is consistent with the predicted location of this motif in the shorter C terminus found in HPEV1. This first structural characterization of a parechovirus indicates that the differences in receptor binding are due to the amino acid differences in the integrins rather than to significantly different viral footprints.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human parechovirus 1 utilizes integrins alphavbeta3 and alphavbeta1 as receptors.J Virol. 2000 Jul;74(13):5856-62. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.13.5856-5862.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10846065 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin alphaVbeta6 is a high-affinity receptor for coxsackievirus A9.J Gen Virol. 2009 Jan;90(Pt 1):197-204. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.004838-0. J Gen Virol. 2009. PMID: 19088289
-
Role of Heparan Sulfate in Cellular Infection of Integrin-Binding Coxsackievirus A9 and Human Parechovirus 1 Isolates.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 19;11(1):e0147168. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147168. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26785353 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of foot-and-mouth disease virus with soluble bovine alphaVbeta3 and alphaVbeta6 integrins.J Virol. 2004 Sep;78(18):9773-81. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.18.9773-9781.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15331710 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Modifications on the αvβ6 Integrin Targeting A20FMDV2 Peptide: A Review.ChemMedChem. 2024 Sep 16;19(18):e202400131. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202400131. Epub 2024 Jul 30. ChemMedChem. 2024. PMID: 38830829 Review.
Cited by
-
Human Parechovirus: an Increasingly Recognized Cause of Sepsis-Like Illness in Young Infants.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2017 Nov 15;31(1):e00047-17. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00047-17. Print 2018 Jan. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2017. PMID: 29142080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and functional analysis of coxsackievirus A9 integrin αvβ6 binding and uncoating.J Virol. 2013 Apr;87(7):3943-51. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02989-12. Epub 2013 Jan 30. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23365426 Free PMC article.
-
Polarized Entry of Human Parechoviruses in the Airway Epithelium.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Aug 22;8:294. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00294. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30211126 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic RNA folding mediates assembly of human parechovirus.Nat Commun. 2017 Feb 23;8(1):5. doi: 10.1038/s41467-016-0011-z. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28232749 Free PMC article.
-
Human Parechovirus 1 Infection Occurs via αVβ1 Integrin.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 29;11(4):e0154769. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154769. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27128974 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abed, Y., and G. Boivin. 2005. Molecular characterization of a Canadian human parechovirus (HPeV)-3 isolate and its relationship to other HPeVs. J. Med. Virol. 77:566-570. - PubMed
-
- Acharya, R., E. Fry, D. Stuart, G. Fox, D. Rowlands, and F. Brown. 1989. The three-dimensional structure of foot-and-mouth disease virus at 2.9 Å resolution. Nature 337:709-716. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

