State-dependent interactions between excitatory neuromodulators in the neuronal control of breathing
- PMID: 20554877
- PMCID: PMC3606074
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5361-09.2010
State-dependent interactions between excitatory neuromodulators in the neuronal control of breathing
Abstract
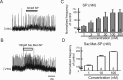
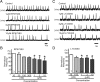
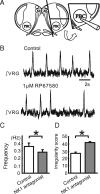
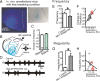
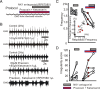
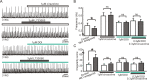
All neuronal networks are modulated by multiple neuropeptides and biogenic amines. Yet, few studies investigate how different modulators interact to regulate network activity. Here we explored the state-dependent functional interactions between three excitatory neuromodulators acting on neurokinin1 (NK1), alpha1 noradrenergic (alpha1 NE), and 5-HT2 serotonin receptors within the pre-Bötzinger complex (pre-BötC), an area critical for the generation of breathing. In anesthetized, in vivo mice, the reliance on endogenous NK1 activation depended on spontaneous breathing frequency and the modulatory state of the animal. Endogenous NK1 activation had no significant respiratory effect when stimulating raphe magnus and/or locus ceruleus, but became critical when alpha1 NE and 5-HT2 receptors were pharmacologically blocked. The dependence of the centrally generated respiratory rhythm on NK1 activation was blunted in the presence of alpha1 NE and 5-HT2 agonists as demonstrated in slices containing the pre-BötC. We conclude that a modulator's action is determined by the concurrent modulation and interaction with other neuromodulators. Deficiencies in one neuromodulator are immediately compensated by the action of other neuromodulators. This interplay could play a role in the state dependency of certain breathing disorders.
Figures





References
-
- Achard P, Zanella S, Rodriguez R, Hilaire G. Perinatal maturation of the respiratory rhythm generator in mammals: from experimental results to computational simulation. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2005;149:17–27. - PubMed
-
- Barthe JY, Clarac F. Modulation of the spinal network for locomotion by substance P in the neonatal rat. Exp Brain Res. 1997;115:485–492. - PubMed
-
- Bernard R, Lydic R, Baghdoyan HA. Hypocretin-1 causes G protein activation and increases ACh release in rat pons. Eur J Neurosci. 2003;18:1775–1785. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
