Shear-induced endothelial cell-cell junction inclination
- PMID: 20554908
- PMCID: PMC2944312
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00156.2010
Shear-induced endothelial cell-cell junction inclination
Abstract
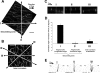
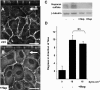
Atheroprone regions of the arterial circulation are characterized by time-varying, reversing, and oscillatory wall shear stress. Several in vivo and in vitro studies have demonstrated that flow reversal (retrograde flow) is atherogenic and proinflammatory. The molecular and structural basis for the sensitivity of the endothelium to flow direction, however, has yet to be determined. It has been hypothesized that the ability to sense flow direction is dependent on the direction of inclination of the interendothelial junction. Immunostaining of the mouse aorta revealed an inclination of the cell-cell junction by 13 degrees in direction of flow in the descending aorta where flow is unidirectional. In contrast, polygonal cells of the inner curvature where flow is disturbed did not have any preferential inclination. Using a membrane specific dye, the angle of inclination of the junction was dynamically monitored using live cell confocal microscopy in confluent human endothelial cell monolayers. Upon application of shear the junctions began inclining within minutes to a final angle of 10 degrees in direction of flow. Retrograde flow led to a reversal of junctional inclination. Flow-induced junctional inclination was shown to be independent of the cytoskeleton or glycocalyx. Additionally, within seconds, retrograde flow led to significantly higher intracellular calcium responses than orthograde flow. Together, these results show for the first time that the endothelial intercellular junction inclination is dynamically responsive to flow direction and confers the ability to endothelial cells to rapidly sense and adapt to flow direction.
Figures




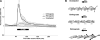
References
-
- Adamson RH, Sarai RK, Weinbaum S, Curry FE. Retrograde shear stress modulates rat mesentery microvessel permeability and endothelial adhesion structures. FASEB J 23: 950–959, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Barbee KA, Mundel T, Lal R, Davies PF. Subcellular distribution of shear stress at the surface of flow-aligned and nonaligned endothelial monolayers. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 268: H1765–H1772, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Butler PJ, Norwich G, Weinbaum S, Chien S. Shear stress induces a time- and position-dependent increase in endothelial cell membrane fluidity. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 280: C962–C969, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Butler PJ, Tsou TC, Li JY, Usami S, Chien S. Rate sensitivity of shear-induced changes in the lateral diffusion of endothelial cell membrane lipids: a role for membrane perturbation in shear-induced MAPK activation. FASEB J 16: 216–218, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

