Oxytocin release in magnocellular nuclei: neurochemical mediators and functional significance during gestation
- PMID: 20554931
- PMCID: PMC3774470
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00217.2010
Oxytocin release in magnocellular nuclei: neurochemical mediators and functional significance during gestation
Abstract
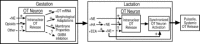
When released from dendrites within the supraoptic (SON) and paraventricular (PVN) nuclei (intranuclear release) during suckling, oxytocin exerts autocrine and paracrine effects on oxytocin neurons that are necessary for the unique timing and episodic pattern of oxytocin release into the systemic circulation that is characteristic of lactation. Recent reports have shown that stimulation of central noradrenergic and histaminergic receptors are both necessary for intranuclear release of oxytocin in response to suckling. In addition, in vitro studies indicate that excitatory amino acids may also be critical for central oxytocin secretion, although in vivo experiments have not provided direct support for this hypothesis. In addition to a critical role in intranuclear oxytocin release during lactation, norepinephrine has also been shown to stimulate central oxytocin during gestation. Stimulation of central oxytocin receptors during gestation appears critical for normal systemic oxytocin secretion in responses to suckling during the subsequent period of lactation. Oxytocin receptor blockade during pregnancy alters normal timing of systemic oxytocin release during suckling and reduces milk delivery. Several adaptations occur in the central oxytocin system that are necessary for determining the unique response characteristic observed during parturition and gestation. Central oxytocin receptor stimulation during gestation has been implicated in pregnancy-related morphological changes in magnocellular oxytocin neurons, disinhibition of oxytocin neurons to GABA, and adaptations in membrane response characteristics of oxytocin neurons. In conclusion, intranuclear oxytocin release during gestation and lactation are critical for establishing, and then evoking the unique pattern of systemic oxytocin secretion in response to the suckling offspring necessary for adequate milk delivery. Furthermore, activation of central noradrenergic receptors appears to be critical for release of central oxytocin in both of these reproductive states.
Figures
References
-
- Amico JA, Crowley RS, Insel TR, Thomas A, O'Keefe JA. Effect of gonadal steroids upon hypothalamic oxytocin expression. Adv Exp Med Biol 395: 23–35, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Bealer SL, Abell SO. Paraventricular nucleus histamine increases blood pressure by adrenoreceptor stimulation of vasopressin release. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 269: H80–H85, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Bealer SL, Crowley WR. Histaminergic control of oxytocin release in the paraventricular nucleus during lactation in rats. Exp Neurol 171: 317–322, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Bealer SL, Crowley WR. Noradrenergic control of central oxytocin release during lactation in rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 274: E453–E458, 1998 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

