Dose combinations of exendin-4 and salmon calcitonin produce additive and synergistic reductions in food intake in nonhuman primates
- PMID: 20554932
- PMCID: PMC2944427
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00275.2010
Dose combinations of exendin-4 and salmon calcitonin produce additive and synergistic reductions in food intake in nonhuman primates
Abstract
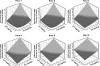
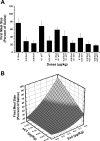
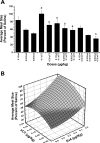
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and amylin mediate the feedback control of eating by seemingly separate, but overlapping mechanisms. This study examined the effects of combined doses of the GLP-1 agonist, exendin-4 (Ex-4), and the amylin analog, salmon calcitonin (sCT), on food intake and meal patterns in adult male rhesus monkeys. Monkeys received intramuscular injections of Ex-4 (0, 0.1, 0.32, or 0.56 microg/kg), sCT (0, 0.1, or 0.32 microg/kg), or combinations thereof before a 6-h daily access to food. Dose combinations produced reductions in food intake that were significantly greater than those produced by the individual doses. Surface plots of the hourly intake indicated a synergistic interaction at lower doses of Ex-4 and sCT during the first 4 h of feeding and additive effects at hours 5 and 6. Meal pattern analysis revealed the combinational doses reduced average meal size and meal frequency by additive interactions, whereas infra-additive effects were apparent at lower doses for first meal size. Combinational doses were further characterized by administration of repeated daily injections of 0.56 microg/kg Ex-4 + 0.32 microg/kg sCT for 5 days. This resulted in sustained reductions in daily food intake (>70% from saline baseline) for 5 days with residual reductions ( approximately 48% from saline baseline) persisting on day 1 following the injections. In contrast, when pair-fed an identical amount of daily food, there was a compensatory food intake increase on day 1 following the pair-feeding ( approximately 132% of saline baseline). Such data suggest Ex-4 and sCT interact in an overall additive fashion to reduce food intake and further the understanding of how GLP-1 and amylin agonist combinations influence feeding behavior.
Figures
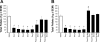
Similar articles
-
The GLP-1 agonist exendin-4 reduces food intake in nonhuman primates through changes in meal size.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007 Sep;293(3):R983-7. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00323.2007. Epub 2007 Jun 20. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17581835
-
Salmon calcitonin reduces food intake through changes in meal sizes in male rhesus monkeys.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008 Jul;295(1):R76-81. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.90327.2008. Epub 2008 May 14. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18480241 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of amylin and salmon calcitonin on feeding and drinking behavior in pygmy goats.Physiol Behav. 2002 Apr 1;75(4):593-9. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9384(02)00655-8. Physiol Behav. 2002. PMID: 12062324
-
Central nervous system pathways targeted by amylin in the regulation of food intake.Biochimie. 2025 Feb;229:95-104. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2024.10.012. Epub 2024 Oct 18. Biochimie. 2025. PMID: 39426704 Review.
-
Exenatide twice daily: a review of its use in the management of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Drugs. 2014 Mar;74(3):325-51. doi: 10.1007/s40265-013-0172-6. Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24435322 Review.
Cited by
-
Citrus aurantium and Rhodiola rosea in combination reduce visceral white adipose tissue and increase hypothalamic norepinephrine in a rat model of diet-induced obesity.Nutr Res. 2013 Jun;33(6):503-12. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2013.04.001. Epub 2013 May 8. Nutr Res. 2013. PMID: 23746567 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-obesity drug discovery: advances and challenges.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022 Mar;21(3):201-223. doi: 10.1038/s41573-021-00337-8. Epub 2021 Nov 23. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022. PMID: 34815532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GLP-1 Based Combination Therapy for Obesity and Diabetes.J Obes Metab Syndr. 2017 Sep;26(3):155-160. doi: 10.7570/jomes.2017.26.3.155. Epub 2017 Sep 30. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2017. PMID: 31089512 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Advancing Translational Understanding for Cancer and Obesity Therapy.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2018 May 9;1(1):2. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.8b00014. eCollection 2018 Sep 14. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2018. PMID: 32219199 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A hippocampus to prefrontal cortex neural pathway inhibits food motivation through glucagon-like peptide-1 signaling.Mol Psychiatry. 2018 Jul;23(7):1555-1565. doi: 10.1038/mp.2017.91. Epub 2017 May 2. Mol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 28461695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aaboe K, Krarup T, Madsbad S, Holst JJ. GLP-1: physiological effects and potential therapeutic applications. Diabetes Obes Metab 10: 994–1003, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Ai G, Chen Z, Shan C, Che J, Hou Y, Cheng Y. Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of exendin-4 in rhesus monkeys. Int J Pharm 353: 56–64, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Brubaker PL, Drucker DJ. Minireview: Glucagon-like peptides regulate cell proliferation and apoptosis in the pancreas, gut, and central nervous system. Endocrinology 145: 2653–2659, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Chan JL, Roth JD, Weyer C. It takes two to tango: combined amylin/leptin agonism as a potential approach to obesity drug development. J Investig Med 57: 777–783, 2009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

