The genetic association between ADHD symptoms and reading difficulties: the role of inattentiveness and IQ
- PMID: 20556504
- PMCID: PMC2964469
- DOI: 10.1007/s10802-010-9429-7
The genetic association between ADHD symptoms and reading difficulties: the role of inattentiveness and IQ
Abstract
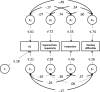
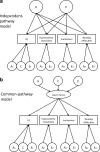
Previous studies have documented the primarily genetic aetiology for the stronger phenotypic covariance between reading disability and ADHD inattention symptoms, compared to hyperactivity-impulsivity symptoms. In this study, we examined to what extent this covariation could be attributed to "generalist genes" shared with general cognitive ability or to "specialist" genes which may specifically underlie processes linking inattention symptoms and reading difficulties. We used multivariate structural equation modeling on IQ, parent and teacher ADHD ratings and parent ratings on reading difficulties from a general population sample of 1312 twins aged 7.9-10.9 years. The covariance between reading difficulties and ADHD inattention symptoms was largely driven by genetic (45%) and child-specific environment (21%) factors not shared with IQ and hyperactivity-impulsivity; only 11% of the covariance was due to genetic effects common with IQ. Aetiological influences shared among all phenotypes explained 47% of the variance in reading difficulties. The current study, using a general population sample, extends previous findings by showing, first, that the shared genetic variability between reading difficulties and ADHD inattention symptoms is largely independent from genes contributing to general cognitive ability and, second, that child-specific environment factors, independent from IQ, also contribute to the covariation between reading difficulties and inattention symptoms.
Figures
References
-
- Alarcon M, DeFries JC. Reading performance and general cognitive ability in twins with reading difficulties and control pairs. Personality and Individual Differences. 1997;22(6):793–803. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8869(96)00267-X. - DOI
-
- American Psychiatric Association (APA) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4 edition, text revision. 4. Washington: APA; 2000.
-
- Astrom R, DeFries JC, Pennington B, Wadsworth S, Willcutt EG. Etiology of covariation between a parent-report screening measure and reading performance. Behavior Genetics. 2009;39(6):634.
-
- Bental B, Tirosh E. The relationship between attention, executive functions and reading domain abilities in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and reading disorder: a comparative study. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry. 2007;48(5):455–463. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2006.01710.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

