Phase II study of S-1, a novel oral fluoropyrimidine, and biweekly administration of docetaxel for previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 20556612
- PMCID: PMC3064900
- DOI: 10.1007/s00280-010-1382-1
Phase II study of S-1, a novel oral fluoropyrimidine, and biweekly administration of docetaxel for previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
Purpose: We examined the safety and efficacy of the combination of S-1 and biweekly docetaxel in patients with previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: Patients with previously treated advanced NSCLC were eligible if they had a performance status of 2 or less, were 80 years or younger, and had adequate organ function. Forty-nine patients (38 men and 11 women; median age, 66 years; range 43-79 years) were enrolled. Patients were treated with the combination of 80 mg/m(2) per day of S-1 for 14 consecutive days and 35 mg/m(2) of docetaxel on days 1 and 15 every 4 weeks.
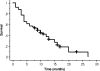
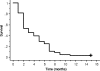
Results: The overall response rate was 16.3% (95% confidence interval, 7.6-30.5%). The disease-control rate was 49.0% (95% confidence interval, 34.4-63.7%). The median survival time after this treatment was 9 months (range 1-22 months). The median progression-free survival time was 3 months (range 1-11 months). Response rates and survival times did not differ significantly according to the histological type. Grade 3-5 toxicities included neutropenia in 51.0% of patients, thrombocytopenia in 2.0%, anemia in 20.4%, infection in 24.5%, anorexia in 12.2%, diarrhea in 14.3%, nausea in 6.1%, and dehydration in 4.2%. There was 1 treatment-related death due to severe anorexia, stomatitis, diarrhea, and, as consequence, dehydration.
Conclusions: The combination of S-1 and biweekly docetaxel is an acceptable therapeutic option in patients with previously treated advanced NSCLC regardless of the histological type.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phase I/II trial of a biweekly combination of S-1 plus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small cell lung cancer (KRSG-0601).Br J Cancer. 2012 Oct 23;107(9):1474-80. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2012.437. Epub 2012 Oct 2. Br J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 23033004 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase II Study of S-1 and Paclitaxel Combination Therapy in Patients with Previously Treated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Oncologist. 2019 Aug;24(8):1033-e617. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0290. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 31040252 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A randomized phase III trial of oral S-1 plus cisplatin versus docetaxel plus cisplatin in Japanese patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: TCOG0701 CATS trial.Ann Oncol. 2015 Jul;26(7):1401-8. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv190. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Ann Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25908605 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized controlled trial of S-1 versus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with platinum-based chemotherapy (East Asia S-1 Trial in Lung Cancer).Ann Oncol. 2017 Nov 1;28(11):2698-2706. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx419. Ann Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29045553 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase I/II study of docetaxel and S-1 in patients with previously treated non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2008 Sep;3(9):1012-7. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318183f8ed. J Thorac Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18758304 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Docetaxel/S-1 Versus Docetaxel/Capecitabine as First-Line Treatment for Advanced Breast Cancer: A Retrospective Study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Oct;94(41):e1340. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001340. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 26469889 Free PMC article.
-
Docetaxel plus S-1 versus docetaxel plus capecitabine as first-line treatment for advanced breast cancer patients: a prospective randomized phase II study.J Natl Cancer Cent. 2023 May 19;3(2):115-120. doi: 10.1016/j.jncc.2023.05.003. eCollection 2023 Jun. J Natl Cancer Cent. 2023. PMID: 39035725 Free PMC article.
-
Phase I/II trial of a biweekly combination of S-1 plus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small cell lung cancer (KRSG-0601).Br J Cancer. 2012 Oct 23;107(9):1474-80. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2012.437. Epub 2012 Oct 2. Br J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 23033004 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
S-1 combined with docetaxel following doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide as neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer: phase II trial.BMC Cancer. 2013 Dec 6;13:583. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-583. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24314307 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase I/II Study of Docetaxel and S-1 in Previously-Treated Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: LOGIK0408.J Clin Med. 2019 Dec 12;8(12):2196. doi: 10.3390/jcm8122196. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31842381 Free PMC article.
References
-
- NSCLC Meta-Analyses Collaborative Group Chemotherapy in addition to supportive care improves survival in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a systemic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data from 16 randomized control trials. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4617–4625. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.17.7162. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shepherd FA, Dancey J, Ramlau R, et al. Prospective randomized trial of docetaxel versus best supportive care in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with platinum-based chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:2095–2103. - PubMed
-
- Fossella FV, Devore R, Kerr RN, et al. Randomized phase III trial of docetaxel versus vinorelbine or ifosfamide in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer previously treated with platinum-containing chemotherapy regimens. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:2354–2362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

