Interventions for cellulitis and erysipelas
- PMID: 20556757
- PMCID: PMC8693180
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004299.pub2
Interventions for cellulitis and erysipelas
Abstract
Background: Cellulitis and erysipelas are now usually considered manifestations of the same condition, a skin infection associated with severe pain and systemic symptoms. A range of antibiotic treatments are suggested in guidelines.
Objectives: To assess the efficacy and safety of interventions for non-surgically-acquired cellulitis.
Search strategy: In May 2010 we searched for randomised controlled trials in the Cochrane Skin Group Specialised Register, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials in The Cochrane Library, MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the ongoing trials databases.
Selection criteria: We selected randomised controlled trials comparing two or more different interventions for cellulitis.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently assessed trial quality and extracted data.
Main results: We included 25 studies with a total of 2488 participants. Our primary outcome 'symptoms rated by participant or medical practitioner or proportion symptom-free' was commonly reported. No two trials examined the same drugs, therefore we grouped similar types of drugs together.Macrolides/streptogramins were found to be more effective than penicillin antibiotics (Risk ratio (RR) 0.84, 95% CI 0.73 to 0.97). In 3 trials involving 419 people, 2 of these studies used oral macrolide against intravenous (iv) penicillin demonstrating that oral therapies can be more effective than iv therapies (RR 0.85, 95% CI 0.73 to 0.98).Three studies with a total of 88 people comparing a penicillin with a cephalosporin showed no difference in treatment effect (RR 0.99, 95% CI 0.68 to 1.43).Six trials which included 538 people that compared different generations of cephalosporin, showed no difference in treatment effect (RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.94 to1.06).We found only small single studies for duration of antibiotic treatment, intramuscular versus intravenous route, the addition of corticosteroid to antibiotic treatment compared with antibiotic alone, and vibration therapy, so there was insufficient evidence to form conclusions. Only two studies investigated treatments for severe cellulitis and these selected different antibiotics for their comparisons, so we cannot make firm conclusions.
Authors' conclusions: We cannot define the best treatment for cellulitis and most recommendations are made on single trials. There is a need for trials to evaluate the efficacy of oral antibiotics against intravenous antibiotics in the community setting as there are service implications for cost and comfort.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures
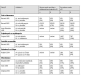


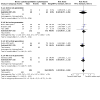


Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Bergkvist 1997 {published data only}
-
- Bergkvist PI, Sjobeck K. Antibiotic and prednisolone therapy of erysipelas: A randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled study. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1997;29(4):377-82. - PubMed
Bernard 1992 {published data only}
-
- Bernard P, Plantin P, Roger H, Sassolas B, Villaret E, Legrain V, et al. Roxithromycin versus penicillin in the treatment of erysipelas in adults: A comparative study. British Journal of Dermatology 1992;127(2):155-9. - PubMed
Bernard 2002 {published data only}
Bucko 2002 part 1 {published data only}
-
- Bucko AD, Hunt BJ, Kidd SL, Hom R. Randomized, double-blind, multicenter comparison of oral cefditoren 200 or 400 mg BID with either cefuroxime 250 mg BID or cefadroxil 500 mg BID for the treatment of uncomplicated skin and skin-structure infections. Clinical Therapeutics 2002;24(7):1134-47. - PubMed
Bucko 2002 part 2 {published data only}
-
- Bucko AD, Hunt BJ, Kidd SL, Hom R. Randomized, double-blind, multicenter comparison of oral cefditoren 200 or 400 mg BID with either cefuroxime 250 mg BID or cefadroxil 500 mg BID for the treatment of uncomplicated skin and skin-structure infections. Clinical Therapeutics 2002;24(7):1134-47. - PubMed
Chan 1995 {published data only}
-
- Chan JC. Ampicillin/sulbactam versus cefazolin or cefoxitin in the treatment of skin and skin-structure infections of bacterial etiology. Advances in Therapy 1995;12(2):139-46. - PubMed
Daniel 1991 part 1 {published data only}
-
- Daniel R. Azithromycin, erythromycin and cloxacillin in the treatment of infections of skin and associated soft tissues. European Azithromycin Study Group. Journal of International Medical Research 1991;19(6):433-45. - PubMed
Daniel 1991 part 2 {published data only}
-
- Daniel R. Azithromycin, erythromycin and cloxacillin in the treatment of infections of skin and associated soft tissues. European Azithromycin Study Group. Journal of International Medical Research 1991;19(6):433-45. - PubMed
DiMattia 1981 {published data only}
-
- DiMattia AF, Sexton MJ, Smialowicz CR, Knapp WH Jr. Efficacy of two dosage schedules of cephalexin in dermatologic infections. Journal of Family Practice 1981;12(4):649-52. - PubMed
Fabian 2005 {published data only}
-
- Fabian TC, File TM Jr, Embil JM, Krige JEJ, Klein S, Rose A, et al. Meropenem versus imipenem-cilastatin for the treatment of hospitalized patients with complicated skin and skin structure infections: Results of a multicenter, randomized, double blind comparative study. Surgical Infections 2005;6(3):269-82. - PubMed
Giordano 2005 {published data only}
-
- Giordano P, Song J, Pertel P, Herrington J, Kowalsky S. Sequential intravenous/oral moxifloxacin versus intravenous piperacillin-tazobactam followed by oral amoxicillin-clavulanate for the treatment of complicated skin and skin structure infection. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 2005;26(5):357-65. - PubMed
Grayson 2002 {published data only}
-
- Grayson ML, McDonald M, Gibson K, Athan E, Munckhof WJ, Paull P, et al. Once-daily intravenous cefazolin plus oral probenecid is equivalent to once-daily intravenous ceftriaxone plus oral placebo for the treatment of moderate-to-severe cellulitis in adults. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2002;34(11):1440-8. - PubMed
-
- Grayson ML, McDonald M, Gibson K, Athan E, Munckhof WJ, Paull P, et al. Once-daily IV cefazolin 2g plus oral probenecid 1g is equivalent to once-daily IV ceftriaxone 1g plus oral placebo for the hospital-in-the-home treatment of cellulitis. Internal Medicine Journal 2001;31:A13.
Hepburn 2004 {published data only}
-
- Hepburn MJ, Dooley DP, Skidmore PJ, Ellis MW, Starnes WF, Hasewinkle WC. Comparison of short-course (5 days) and standard (10 days) treatment for uncomplicated cellulitis. Archives of Internal Medicine 2004;164(15):1669-74. - PubMed
Iannini 1985 {published data only}
-
- Iannini PB, Kunkel MJ, Link ASJ, Simons WJ, Lee TJ, Tight RR. Multicenter comparison of cefonicid and cefazolin in hospitalized patients with skin and soft tissue infections. Advances in Therapy 1985;2(5):214-24.
Johnson 2007 {published data only}
-
- Johnson S, Leak K, Singh S, Tan P, Pillay W, Cuschieri R. Can cycloidal vibration plus standard treatment reduce lower limb cellulitis treatment times? Journal of Wound Care 2007;16(4):166-9. - PubMed
Kiani 1991 {published data only}
-
- Kiani R. Double-blind, double-dummy comparison of azithromycin and cephalexin in the treatment of skin and skin structure infections. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases 1991;10(10):880-4. - PubMed
Leman 2005 {published data only}
Rao 1985 {published data only}
-
- Rao B, See RC, Chuah Sk, Bansal MB, Lou MA, Thadepalli H. Ticarcillin plus calvulanic acid versus moxalactam in the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections. The American Journal of Medicine 1985;79 Suppl 2(5):126-9. - PubMed
Sachs 1990 {published data only}
-
- Sachs MK, Pilgrim C. Ampicillin/sulbactam compared with cefazolin or cefoxitin for the treatment of skin and skin structure infections. Drug Investigation 1990;2(3):173-83.
Schwartz 1996 {published data only}
-
- Schwartz R, Das-Young LR, Ramirez-Ronda C, Frank E. Current and future management of serious skin and skin-structure infections. American Journal of Medicine 1996;100(6A):90S-5S. - PubMed
Tack 1998 {published data only}
-
- Tack KJ, Littlejohn TW, Mailloux G, Wolf MM, Keyserling CH. Cefdinir versus cephalexin for the treatment of skin and skin-structure infections. The Cefdinir Adult Skin Infection Study Group. Clinical Therapeutics 1998;20(2):244-56. - PubMed
Tarshis 2001 {published data only}
-
- Tarshis GA, Miskin BM, Jones TM, Champlin J, Wingert KJ, Breen JD, et al. Once-daily oral gatifloxacin versus oral levofloxacin in treatment of uncomplicated skin and soft tissue infections: Double blind, multicenter, randomized study. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2001;45(8):2358-62. - PMC - PubMed
Vinen 1996 {published data only}
-
- Vinen J, Hudson B, Chan B, Fernandes C. A randomised comparative study of once-daily ceftriaxone and 6-hourly flucloxacillin in the treatment of moderate to severe cellulitis. Clinical efficacy, safety and pharmacoeconomic implications. Clinical Drug Investigation 1996;12(5):221-5.
Weigelt 2005 {published data only}
Zeglaoui 2004 {published data only}
-
- Zeglaoui F, Dziri C, Mokhtar I, Ezzine N, Kharfi M, Zghal M, et al. Intramuscular bipenicillin vs. intravenous penicillin in the treatment of erysipelas in adults: Randomized controlled study. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (JEADV) 2004;18(4):426-8. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Agache 1987 a {published data only}
-
- Agache P, Amblard P, Moulin G, Barrière H, Texier L, Beylot C, et al. Roxithromycin in skin and soft tissue infections. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1987;20 Suppl B:153-6. - PubMed
Agache 1987 b {published data only}
-
- Agache P, Amblard P, Moulin G, Barrière H, Texier L, Beylot C, et al. Roxithromycin in skin and soft tissue infections. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1987;20 Suppl B:153-6. - PubMed
Amaya‐Tapia 1992 {published data only}
-
- Amaya-Tapia G, Andrade-Villanueva J, Flores-Glaxiola A, Aguirre-Avalos G, Morfin-Otero R, Esparza-Ahumada S. Safety and efficacy of lomefloxacin and cefaclor in the treatment of skin and skin structure infections. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 1992;2(1):55-60. - PubMed
Amaya‐Tapia 1993 {published data only}
-
- Amaya-Tapia G, Aguirre-Avalos G, Andrade-Villanueva J, Peredo-González G, Morfín-Otero R, Esparza-Ahumada S, et al. Once-daily azithromycin in the treatment of adult skin and skin-structure infections. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1993;31 Suppl E:129-35. - PubMed
Arata 1989 {published data only}
-
- Arata J, Yamamoto Y, Tamaki H, Ookawara A, Fukaya T, Ishibashi Y, et al. Double-blind study of lomefloxacin vs. norfloxacin in the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections. Chemotherapy 1989;37(4):482-503.
Arata 1994 a {published data only}
-
- Arata J, Akiyama H, Abe Y, Ishibashi Y, Takehara K, Tsuchida T, et al. A double-blind comparative study of S-1108 and cefaclor in skin and skin structure infections. Chemotherapy 1994;42(3):326-45.
Arata 1994 b {published data only}
-
- Arata J, Kanzaki H, Abe Y, Torigoe R, Ohkawara A, Yamanaka K, et al. A multicenter, double-blind, double-placebo comparative study of SY 5555 versus cefaclor in the treatment of skin and skin structure infections. Chemotherapy 1994;42(6):740-60.
Arata 1995 {published data only}
-
- Arata J, Torigoe R, Ohkawara A, et al. A multicenter, double-blind, double placebo clinical trial of azithromycin versus cefaclor in the treatment of skin and skin structure infections. Japanese Journal of Chemotherapy 1995;43(11):1069-87.
Azimi 1999 {published data only}
-
- Azimi PH, Barson WJ, Janner D, Swanson R. Efficacy and safety of ampicillin/sulbactam and cefuroxime in the treatment of serious skin and skin structure infections in pediatric patients. UNASYN Pediatric Study Group. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 1999;18(7):609-13. - PubMed
Ballantyne 1980 {published data only}
-
- Ballantyne F. A comprehensive study of cefadroxil and cephalexin in the treatment of soft tissue infections. Journal of International Medical Research 1980;8 Suppl 1:70-4. - PubMed
Ballantyne 1985 {published data only}
-
- Ballantyne FN. Comparative efficacy of cefadroxil and cefaclor in the treatment of skin and soft-tissue infections. Clinical Therapeutics 1985;7(4):487-91. - PubMed
Bechard 1984 {published data only}
-
- Bechard DL, Hawkins SH, Sutherland SC. Comparative evaluation of cefmenoxime versus cefoxitin in serious infections. American Journal of Medicine 1984;77(6A):13-6. - PubMed
Bergkvist 1998 {published data only}
-
- Bergkvist PI, Sjobeck K. Relapse of erysipelas following treatment with prednisolone or placebo in addition to antibiotics: A 1-year follow-up. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1998;30(2):206-7. - PubMed
Blaszczyk‐Kostanecka {published data only}
-
- Blaszczyk-Kostanecka M, Dobozy A, Dominguez-Soto L, Guerrero R, Hunyadi J, Lopera J, et al. Comparison of two regimens of oral clindamycin versus dicloxacillin in the treatment of mild-to-moderate skin and soft-tissue infections. Current Therapeutic Research - Clinical and Experimental 1998;59(6):341-53.
Bradsher 1984 {published data only}
-
- Bradsher RW Jr, Snow RM. Ceftriaxone treatment of skin and soft tissue infections in a once daily regimen. American Journal of Medicine 1984;77(4C):63-7. - PubMed
Breedt 2005 {published data only}
-
- Breedt J, Teras J, Gardovskis J, Maritz FJ, Vaasna T, Ross DP, et al. Safety and efficacy of tigecycline in treatment of skin and skin structure infections: Results of a double-blind phase 3 comparison study with vancomycin-aztreonam. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2005;49(11):4658-66. - PMC - PubMed
Brown 1996 {published data only}
-
- Brown G, Chamberlain R, Goulding J, Clarke A. Ceftriaxone versus cefazolin with probenecid for severe skin and soft tissue infections. Journal of Emergency Medicine 1996;14(5):547-51. - PubMed
Browning 1981 {published data only}
-
- Browning AK. The efficacy of twice daily cephalexin. Pharmatherapeutica 1981;2(9):559-64. - PubMed
Carbon 1992 {published data only}
-
- Carbon C. Prospective randomized phase II study of intravenous cefpirome 1g or 2g bd in the treatment of hospitalized patients with different infections. Cefpirome Study Group. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1992;29 Suppl A:87-94. - PubMed
Carbon 1995 {published data only}
-
- Carbon C. Overview of the efficacy of isepamicin in the adult core clinical trial programme. Journal of Chemotherapy 1995;7 Suppl 2:79-85. - PubMed
Carr 1994 {published data only}
-
- Carr WD, Wall AR, Georgala-Zervogiani S, Stratigos J, Gouriotou K. Fusidic acid tablets in patients with skin and soft-tissue infection: A dose-finding study. European Journal of Clinical Research 1994;5:87-95.
Chiodini 1985 {published data only}
-
- Chiodini PL, Toop MJ, Odugbesan O, Gilbert J, Farrell ID, Barnett AH, et al. Sulbactam/ampicillin: Effects on glucose metabolism in diabetics with soft tissue infection. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1985;16(5):643-7. - PubMed
Chirurgi 1994 {published data only}
-
- Chirurgi VA, Edelstein H, Oster SE, Karp R, Cassano KB, Aiken S, et al. Randomized comparison trial of teicoplanin i.v., teicoplanin i.m., and cefazolin therapy for skin and soft tissue infections caused by gram-positive bacteria. Southern Medical Journal 1994;87(9):875-80. - PubMed
Colardyn 1996 {published data only}
-
- Colardyn F, Faulkner KL. Intravenous meropenem versus imipenem/cilastatin in the treatment of serious bacterial infections in hospitalized patients. Meropenem Serious Infection Study Group. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1996;38(3):523-37. - PubMed
Colin 1988 {published data only}
-
- Colin M, Avon P. Comparative double-blind evaluation of a new topical antibacterial agent, mupirocin, compared with placebo in the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections [Evaluation comparative double aveugle du nouvel agent antibacterien topique, la mupirocine, par rapport a un placebo dans le traitement des infections de la peau et des tissus mous]. Pharmatherapeutica 1988;5(3):198-203. - PubMed
Daly 1990 {published data only}
Derriennic 1993 {published data only}
-
- Derriennic M, Escande JP. Dirithromycin in the treatment of skin and skin structure infections. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1993;31 Suppl C:159-68. - PubMed
Echols 1994 {published data only}
-
- Echols R, Coulter H. Efficacy and safety of IV ciprofloxacin versus standard antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of selected tissue infections. Infections in Medicine 1994;11(6):461-9.
Edelstein 1991 {published data only}
-
- Edelstein H, Oster SE, Chirurgi VA, Karp RA, Cassano KB, McCabe RE. Intravenous or intramuscular teicoplanin once daily for skin and soft-tissue infections. DICP : the annals of pharmacotherapy 1991;25(9):914-8. - PubMed
Eron 1983 {published data only}
Fass 1989 {published data only}
-
- Fass RJ, Plouffe JF, Russell JA. Intravenous/oral ciprofloxacin versus ceftazidime in the treatment of serious infections. American Journal of Medicine 1989;87(5A):164S-8S. - PubMed
File 1991 {published data only}
-
- File TM Jr, Tan JS. Ticarcillin-clavulanate therapy for bacterial skin and soft tissue infections. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1991;13 Suppl 9:S733-6. - PubMed
Fleisher 1983 {published data only}
Frank 1989 {published data only}
-
- Frank E, Phillips SL, Gupta T, Bavishi N, Casey KK. Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections: A comparative study of cefmetazole and cefoxitin. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1989;23 Suppl D:55-60. - PubMed
Fujita 1985 {published data only}
-
- Fujita K, Takahashi H, Mizoguchi A, Takeshima M, Sasaki J, Nonami E, et al. Clinical evaluation of lenampicillin in the treatment of superficial suppurative skin and soft tissue infection. A double-blind study compared to amoxicillin. Japanese Journal of Antibiotics 1985;38(7):1794-818. - PubMed
Geckler 1988 {published data only}
-
- Geckler RW, Eng RH, Fabian TC, Echols RM, Jemsek JG, LeFrock JL. A multicenter comparative study of cefotetan once daily and cefoxitin thrice daily for the treatment of infections of the skin and superficial soft tissue. American Journal of Surgery 1988;155(5A):91-5. - PubMed
Gentry 1989 a {published data only}
-
- Gentry LO, Rodriguez-Gomez G, Zeluff BJ, Khoshdel A, Price M. A comparative evaluation of oral ofloxacin versus intravenous cefotaxime therapy for serious skin and skin structure infections. American Journal of Medicine 1989;87(6C):57S-60S. - PubMed
Gentry 1989 b {published data only}
-
- Gentry LO, Ramirez-Ronda CH, Rodriguez-Noriega E, Thadepalli H, Del Rosal PL, Ramirez C. Oral ciprofloxacin vs parenteral cefotaxime in the treatment of difficult skin and skin structure infections. A multicenter trial. Archives of Internal Medicine 1989;149(11):2579-83. - PubMed
Gentry 1996 {published data only}
-
- Gentry LO, Rodriguez-Gomez G, Pien F, Cubeddu L, Holley HP Jr, Buaron K, et al. Comparative effects of ceftazidime two or three times daily in patients with skin and skin structure infections. American Journal of Therapeutics 1996;3(3):212-8. - PubMed
Gesser 2004 a {published data only}
-
- Gesser RM, McCarroll KA, Woods GL. Efficacy of ertapenem against methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in complicated skin/skin structure infections: Results of a double-blind clinical trial versus piperacillin-tazobactam. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 2004;23(3):235-9. - PubMed
Gesser 2004 b {published data only}
-
- Gesser RM, McCarroll KA, Woods GL. Evaluation of outpatient treatment with ertapenem in a double blind controlled clinical trial of complicated skin/skin structure infections. The Journal of Infection 2004;48(1):32-8. - PubMed
Gordin 1985 {published data only}
Gould 1988 {published data only}
-
- Gould IM, Hudson M, Morris J, Page G, Douglas JG, Smith CC, et al. Imipenem versus standard therapy in the treatment of serious soft tissue infection. Drugs Under Experimental & Clinical Research 1988;14(8):555-8. - PubMed
Graham 2002 {published data only}
-
- Graham DR, Talan DA, Nichols RL, Lucasti C, Corrado M, Morgan N, et al. Once-daily, high-dose levofloxacin versus ticarcillin-clavulanate alone or followed by amoxicillin-clavulanate for complicated skin and skin-structure infections: A randomized, open-label trial. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2002;35(4):381-9. - PubMed
Hanfling 1992 {published data only}
-
- Hanfling MJ, Hausinger SA, Squires J. Loracarbef vs. cefaclor in pediatric skin and skin structure infections. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 1992;11(8 Suppl):S27-30. - PubMed
Henry 1985 {published data only}
-
- Henry SA, Bendush CB. Aztreonam: Worldwide overview of the treatment of patients with gram-negative infections. American Journal of Medicine 1985;78(2a):57-64. - PubMed
Hubsher 1976 {published data only}
-
- Hubsher JA, Gadebusch HH, Itkin AG. Double-blind comparison of cephradine and cephalexin in the treatment of skin and soft-tissue infections due to Staphylococcus aureus. Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical & Experimental 1976;19(6):579-88. - PubMed
Jorup‐Rönström 1984 {published data only}
-
- Jorup-Rönström C, Britton S, Gavlevik A, Gunnarsson K, Redman AC. The course, costs and complications of oral versus intravenous penicillin therapy of erysipelas. Infection 1984;12(6):390-4. - PubMed
Kulhanjian 1989 {published data only}
-
- Kulhanjian J, Dunphy MG, Hamstra S, Levernier K, Rankin M, Petru A, et al. Randomized comparative study of ampicillin/sulbactam vs. ceftriaxone for treatment of soft tissue and skeletal infections in children. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 1989;8(9):605-10. - PubMed
Lobo 1995 {published data only}
-
- Lobo JM, Guedes MM. Treatment of bacterial skin infections. An open, randomized and comparative study among roxithromycin and cephalexin. Revista Brasileira de Medicina 1995;52(9):1047-51.
Miller 1989 {published data only}
-
- Miller LM, Mooney CJ, Hansbrough JF. Comparative evaluation of cefaclor versus cefadroxil in the treatment of skin and skin structure infections. Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical and Experimental 1989;46(3):405-10.
Nolen 1992 {published data only}
-
- Nolen T, Conetta BJ, Durham SJ, Wilber RB. Safety and efficacy of cefprozil vs cefaclor in the treatment of mild to moderate skin and skin structure infections. Infections in Medicine 1992;9 Suppl C:56-68. - PubMed
Parish 1984 {published data only}
-
- Parish LC, Parks DB, Layne PP, Uri JV. Ceftizoxime treatment of cutaneous and subcutaneous tissue infections. Clinical Therapeutics 1984;6(5):613-9. - PubMed
Parish 1991 {published data only}
-
- Parish LC, Jungkind DL. Systemic antimicrobial therapy in skin and skin structure infections: Comparison of temafloxacin and ciprofloxacin. American Journal of Medicine 1991;91(6A):115S-9S. - PubMed
Parish 1993 {published data only}
-
- Parish LC. Clarithromycin in the treatment of skin and skin structure infections: Two multicenter clinical studies. Clarithromycin Study Group. International Journal of Dermatology 1993;32(7):528-32. - PubMed
Parish 1993a {published data only}
-
- Parish LC, Jungkind DL. Systemic antimicrobial therapy for skin and skin structure infections: Comparison of fleroxacin and ceftazidime. American Journal of Medicine 1993;94(3A):166S-73S. - PubMed
Pereira 1996 {published data only}
-
- Pereira LC. Comparative clinical study between roxithromycin and cephalexin in the treatment of folliculitis, furunculosis and Erysipelas /Cellulitis. Revista Brasileira De Medicina 1996;53(1-2):81-6.
Perez‐Ruvalcaba 1987 {published data only}
-
- Pérez-Ruvalcaba JA, Quintero-Pérez NP, Morales-Reyes JJ, Huitrón-Ramirez JA, Rodriguez-Chagollán JJ, Rodríguez-Noriega E. Double-blind comparison of ciprofloxacin with cefotaxime in the treatment of skin and skin structure infections. American Journal of Medicine 1987;82(4A):242-6. - PubMed
Pien 1983 {published data only}
Ramirez‐Ronda 1982 {published data only}
-
- Ramírez-Ronda CH, Gutíerrez J, Bermúdez RH. Comparative effectiveness, safety and tolerance of mezlocillin and ticarcillin: A prospective randomized trial. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1982;9 Suppl A:125-9. - PubMed
Ramirez‐Ronda 1987 {published data only}
-
- Ramirez-Ronda CH, Saavedra S, Rivera-Vázquez CR. Comparative, double-blind study of oral ciprofloxacin and intravenous cefotaxime in skin and skin structure infections. American Journal of Medicine 1987;82(4A):220-3. - PubMed
Sacchidanand 2005 {published data only}
-
- Sacchidanand S, Penn RL, Embil JM, Campos ME, Curcio D, Ellis-Grosse E, et al. Efficacy and safety of tigecycline monotherapy compared with vancomycin plus aztreonam in patients with complicated skin and skin structure infections: Results from a phase 3, randomized, double-blind trial. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2005;9(5):251-61. - PubMed
Schupbach 1992 {published data only}
-
- Schupbach CW, Olovich KG, Dere WH. Efficacy of cefaclor AF in the treatment of skin and skin-structure infections. Clinical Therapeutics 1992;14(3):470-9. - PubMed
Segev 1990 {published data only}
-
- Segev S, Rosen N, Pitlik SD, Block C, Rubinstein E. Pefloxacin versus ceftazidime in therapy of soft tissue infections in compromised patients. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1990;26 Suppl B:193-8. - PubMed
Siami 2001 {published data only}
Solomkin 1986 {published data only}
-
- Solomkin JS, Cocchetto DM. Ceftazidime versus tobramycin plus ticarcillin in the treatment of soft-tissue infections. Clinical Therapeutics 1986;9(1):123-34. - PubMed
Stevens 2000 {published data only}
Tan 1993 {published data only}
-
- Tan JS, Wishnow RM, Talan DA, Duncanson FP, Norden CW. Treatment of hospitalized patients with complicated skin and skin structure infections: Double-blind, randomized, multicenter study of piperacillin-tazobactam versus ticarcillin-clavulanate. The Piperacillin/Tazobactam Skin and Skin Structure Study Group. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1993;37(8):1580-6. - PMC - PubMed
Tassler 1993 {published data only}
-
- Tassler H. Comparative efficacy and safety of oral fleroxacin and amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium in skin and soft tissue infections. American Journal of Medicine 1993;94(3A):159S-65S. - PubMed
Wasilewski 2000 {published data only}
-
- Wasilewski MM, Wilson MG, Sides GD, Stotka JL. Comparative efficacy of 5 days of dirithromycin and 7 days of erythromycin in skin and soft tissue infections. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2000;46(2):255-62. - PubMed
Wible 2003 {published data only}
-
- Wible K, Tregnaghi M, Bruss J, Fleishaker D, Naberhuis-Stehouwer S, Hilty M. Linezolid versus cefadroxil in the treatment of skin and skin structure infections in children. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2003;22(4):315-23. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Chaudhary 2008 {published data only}
-
- Chaudhary M, Shrivastava SM, Sehgal R. Efficacy and safety study of fixed-dose combination of ceftriaxone-vancomycin injection in patients with various infections. Current Drug Safety 2008;3(1):82-85. - PubMed
Manaktala 2009 {published data only}
Nichols 1999 {published data only}
-
- Nichols RL, Graham DR, Barriere SL, Rodgers A, Wilson SE, Zervos M, et al. Treatment of hospitalized patients with complicated gram-positive skin and skin structure infections: Two randomized, multicentre studies of quinupristin/dalfopristin versus cefazolin, oxacillin or vancomycin. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1999;44(2):263-273. - PubMed
Noel 2008 {published data only}
-
- Noel GJ, Bush K, Bagchi P, Lanus J, Strauss RS. A randomized, double-blind trial comparing ceftobiprole medocaril with vancomycin plus ceftazidime for the treatment of patients with complicated skin and skin-structure infections. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2008;46(5):647-655. - PubMed
Pertel 2009 {published data only}
Snodgrass 1937 {published data only}
Snodgrass WR 1937 {published data only}
Stein 2008 {published data only}
-
- Stein GE, Schooley SL, Havlichek DH, Nix DE. Outpatient intravenous antibiotic therapy compared with oral linezolid in patients with skin and soft tissue infections: A pharmacoeconomic analysis. Infectious Diseases in Clinical Practice 2008;16(4):235-239.
References to ongoing studies
ISRCTN76443564 {unpublished data only}
-
- ISRCTN76443564. The efficacy and safety evaluation of ceftriaxone and sulbactam combination (1.5 gram) in patients with skin and soft tissue infections: An open label, parallel, randomized, prospective comparative trial. ISRCTN Register.
NCT00295178 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT00295178. A Multicenter, Randomized Study Comparing CUBICIN® (Daptomycin for injection) with Vancomycin in the treatment of cellulitis or erysipelas. World Health Organisation International Clinical Trials Registry.
NCT00424190 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT00424190. Comparative study of ceftaroline vs. vancomycin plus aztreonam in adult subjects with complicated skin infections. ClinicalTrials.gov (accessed May 2010).
NCT00948142 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT00948142. Safety and efficacy of CEM-102 compared to linezolid in acute bacterial skin infections. ClinicalTrials.gov (accessed May 2010).
Additional references
Altman 2001
Ambati 2000
-
- Ambati BK, Ambati J, Azar N, Stratton L, Schmidt EV. Periorbital and orbital cellulitis before and after the advent of Haemophilus influenzae type B vaccination. Ophthalmology 2000;107(8):1450-1453. - PubMed
Baddour 1984
-
- Baddour LM, Bisno AL. Recurrent cellulitis after coronary bypass surgery. Association with superficial fungal infection in saphenous venectomy limbs. JAMA 1984;251(8):1049-52. - PubMed
Bernard 1987
-
- Bernard P, Toty L, Mounier M, Denis F, Bonnetblanc JM. Early detection of streptococcal group antigens in skin samples by latex particle agglutination. Archives of Dermatology 1987;123(4):468-70. - PubMed
British Lymphology Society 2007
-
- British Lymphology Society. Consensus Document on the Management of Cellulitis in Lymphoedema. www.lymphoedema.org/lsn/ (accessed July 2007).
Brook 1995
-
- Brook I, Frazier EH. Clinical features and aerobic and anaerobic microbiological characteristics of cellulitis. Archives of Surgery (Chicago, Ill. : 1960) 1995;130(7):786-92. - PubMed
Carter 2007
-
- Carter K, Kilburn S, Featherstone P. Cellulitis and treatment: A qualitative study of experiences. British Journal of Nursing 2007;16(6):S22-4, S26-8. - PubMed
Chan R 1995
Corwin 2005
Cox 1998
Cox 2006
-
- Cox MH. Oedema as a risk factor for multiple episodes of cellulitis/erysipelas of the lower leg: A series with community follow-up. British Journal of Dermatology 2006;155(5):947-50. - PubMed
CREST 2005
-
- Clinical Resource Efficiency Support Team (CREST). Guidelines on the management of cellulitis in adults. http//www.crestni.org.uk 2005. [ISBN 1-903982-12-X]
Critchley 1997
Dupuy 1999
Ellis Simonsen 2006
Eriksson 1996
-
- Eriksson B, Jorup-Rönström C, Karkkonen K, Sjöblom AC, Holm SE. Erysipelas: Clinical and bacteriologic spectrum and serological aspects. Clinical Infectious Diseases 1996;23(5):1091-8. - PubMed
Eron 2003
-
- Eron LJ, Lipsky BA, Low DE, Nathwani D, Tice AD, Volturo GA, et al. Managing skin and soft tissue infections: Expert panel recommendations on key decision points. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2003;52 Suppl 1:i3-17. - PubMed
Escalante 1995
-
- Escalante A, Beardmore TD. Risk factors for early wound complications after orthopedic surgery for rheumatoid arthritis. The Journal of Rheumatology 1995;22(10):1844-51. - PubMed
Haan 1997
-
- Haan MN, Selby JV, Quesenberry CP Jr, Schmittdiel JA, Fireman BH, Rice DP. The impact of ageing and chronic disease on use of hospital and outpatient services in a large HMO: 1971-1991. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1997;45(6):667-74. - PubMed
Hay 2004
-
- Hay RJ, Adriaans BM. Bacterial Infections. In: Burns DA, Breathnach SM, Cox NH, Griffiths CEM, editors(s). Rook's Textbook of Dermatology. 7th edition. Vol. 1. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing, 2004:27.16-27.20.
Higgins 2008
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, 2008.
Hoberman 1999
-
- Hoberman A, Wald ER, Hicky RW, Baskin M, Charron M, Masoud M, et al. Oral versus initial intravenous therapy for urinary tract infections in young febrile children. Pediatrics 1999;104:79-86. - PubMed
Jorup‐Rönström 1987
-
- Jorup-Rönström C, Britton S. Recurrent erysipelas: Predisposing factors and costs of prophylaxis. Infection 1987;15(2):105-6. - PubMed
Jüni 2001
Kern 1999
-
- Kern WV, Cometta A, De Bock R, Langenaeken J, Paesmans M, Gaya H. Oral versus intravenous empirical antimicrobial therapy for fever in patients with granulocytopenia who are receiving cancer chemotherapy. New England Journal of Medicine 1999;341(5):312-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kluytmans‐Vandenbergh 2006
-
- Kluytmans-Vandenbergh MF, Kluytmans JA. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Current perspectives. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2006;12 Suppl 1:9-15. - PubMed
Lasley 1997
-
- Lasley DS, Eblen A, Yancey MK, Duff P. The effect of placental removal method on the incidence of postcesarean infections. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 1997;176(6):1250-4. - PubMed
Mokni 2006
-
- Mokni M, Dupuy A, Denguezli M, Dhaoui R, Bouassida S, Amri M, et al. Risk factors for erysipelas of the leg in Tunisia: A multicenter case-control study. Dermatology 2006;212(2):108-12. - PubMed
Morris 2001
-
- Morris A. Cellulitis and Erysipelas. In: BMJ editorial board, editors(s). Clinical Evidence. London: BMJ Books, 2001:1146-9.
PATCH I and II
-
- ISRCTN34716921 (PATCH I), ISRCTN03813200 (PATCH II), UKDCTN0501. Randomised controlled trials to investigate whether prophylactic antibiotics can prevent further episodes of cellulitis (erysipelas) of the leg. clinicaltrials.gov.
Pavlotsky 2004
-
- Pavlotsky F, Amrani S, Trau H. Recurrent erysipelas: Risk factors. Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft 2004;2(2):89-95. - PubMed
Purcell 2005
-
- Purcell K, Fergie J. Epidemic of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections: A 14-year study at Driscoll Children's Hospital. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2005;159(10):980-85. - PubMed
Rojas 2006
Roujeau 2004
-
- Roujeau JC, Sigurgeirsson B, Korting HC, Kerl H, Paul C. Chronic dermatomycoses of the foot as risk factors for acute bacterial cellulitis of the leg: A case-control study. Dermatology 2004;209(4):301-7. - PubMed
Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain 2007
-
- Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain. British National Formulary. London: BMJ Publishing Group Ltd and RPS Publishing, 2007.
Societe Francaise de Dermatologie 2001
-
- Societe Francaise de Dermatologie. Erysipelas and necrotizing fasciitis [Erysipele et fasiite necrosante: prise en charge]. Annales de dermatologie et de vénéréologie 2001;128:463-82. - PubMed
Soo 2008
-
- Soo J K, Bicanic T A, Heenan S, Mortimer P S. Lymphatic abnormalities demonstrated by lymphoscintigraphy after lower limb cellulitis. British Journal of Dermatology 2008;158(6):1350-53. - PubMed
Stevens 2005
-
- Stevens DL, Bisno AL, Chambers HF, Everett ED, Dellinger P, Goldstein EJ, et al. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of skin and soft-tissue infections. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2005;41(10):1373-406. - PubMed
Thomas 1999
-
- Thomas TA, Taylor SM, Crane MM, Cornett WR, Langan EM 3rd, Snyder BA, et al. An analysis of limb-threatening lower extremity wound complications after 1090 consecutive coronary artery bypass procedures. Vascular medicine (London, England) 1999;4(2):83-8. - PubMed
UK DOH 2001
-
- United Kingdom Department of Health. Hospital Episode Statistics 2001. www.statistics.gov.uk (accessed June 2003).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

