Shear wave velocity is a useful marker for managing nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- PMID: 20556839
- PMCID: PMC2887589
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i23.2918
Shear wave velocity is a useful marker for managing nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Abstract
Aim: To investigate whether a noninvasive measurement of tissue strain has a potential usefulness for management of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Methods: In total 26 patients, 23 NASHs and 3 normal controls were enrolled in this study. NASH was staged based on Brunt criterion. At a region of interest (ROI), a shear wave was evoked by implementing an acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI), and the propagation velocity was quantified.
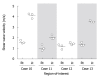
Results: Shear wave velocity (SWV) could be reproducibly quantified at all ROIs in all subjects except for 4 NASH cases, in which a reliable SWV value was not calculated at several ROIs. An average SWV of 1.34 +/- 0.26 m/s in fibrous stage 0-1 was significantly slower than 2.20 +/- 0.74 m/s and 2.90 +/- 1.01 m/s in stages 3 and 4, respectively, but was not significantly different from 1.79 +/- 0.78 m/s in stage 2. When a cutoff value was set at 1.47 m/s, receiver operating characteristic analysis showed significance to dissociate stages 3 and 4 from stage 0-1 (P = 0.0092) with sensitivity, specificity and area under curve of 100%, 75% and 94.2%, respectively. In addition, the correlation between SWV and hyaluronic acid was significant (P < 0.0001), while a tendency toward negative correlation was observed with serum albumin (P = 0.053).
Conclusion: The clinical implementation of ARFI provides noninvasive repeated evaluations of liver stiffness at an arbitrary position, which has the potential to shed new light on NASH management.
Figures


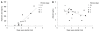
References
-
- Torres DM, Harrison SA. Diagnosis and therapy of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:1682–1698. - PubMed
-
- Rockey DC, Caldwell SH, Goodman ZD, Nelson RC, Smith AD. Liver biopsy. Hepatology. 2009;49:1017–1044. - PubMed
-
- Sandrin L, Fourquet B, Hasquenoph JM, Yon S, Fournier C, Mal F, Christidis C, Ziol M, Poulet B, Kazemi F, et al. Transient elastography: a new noninvasive method for assessment of hepatic fibrosis. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2003;29:1705–1713. - PubMed
-
- Aguirre DA, Behling CA, Alpert E, Hassanein TI, Sirlin CB. Liver fibrosis: noninvasive diagnosis with double contrast material-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology. 2006;239:425–437. - PubMed
-
- Foucher J, Castéra L, Bernard PH, Adhoute X, Laharie D, Bertet J, Couzigou P, de Lédinghen V. Prevalence and factors associated with failure of liver stiffness measurement using FibroScan in a prospective study of 2114 examinations. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;18:411–412. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

