H2S mediates O2 sensing in the carotid body
- PMID: 20556885
- PMCID: PMC2890835
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1005866107
H2S mediates O2 sensing in the carotid body
Abstract
Gaseousmessengers, nitric oxide and carbon monoxide, have been implicated in O2 sensing by the carotid body, a sensory organ that monitors arterial blood O2 levels and stimulates breathing in response to hypoxia. We now show that hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a physiologic gasotransmitter of the carotid body, enhancing its sensory response to hypoxia. Glomus cells, the site of O2 sensing in the carotid body, express cystathionine gamma-lyase (CSE), an H2S-generating enzyme, with hypoxia increasing H2S generation in a stimulus-dependent manner. Mice with genetic deletion of CSE display severely impaired carotid body response and ventilatory stimulation to hypoxia, as well as a loss of hypoxia-evoked H2S generation. Pharmacologic inhibition of CSE elicits a similar phenotype in mice and rats. Hypoxia-evoked H2S generation in the carotid body seems to require interaction of CSE with hemeoxygenase-2, which generates carbon monoxide. CSE is also expressed in neonatal adrenal medullary chromaffin cells of rats and mice whose hypoxia-evoked catecholamine secretion is greatly attenuated by CSE inhibitors and in CSE knockout mice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
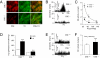
 ∼ 39 mmHg; at black bar) in CSE +/+ and CSE−/− mice. Integrated carotid body sensory activity (CB activity) is presented as impulses per second (imp/s). Superimposed action potentials from the single fiber are presented in Inset. (C) Carotid body responses to graded hypoxia from CSE+/+ and CSE−/− mice, measured as the difference in response between baseline and hypoxia (Δimp/s). Data are mean ± SEM of n = 24 (CSE+/+) and n = 23 (CSE−/−) fibers from eight mice each. (D) H2S levels (mean ± SEM) in carotid bodies from CSE+/+ and CSE−/− mice under normoxia (NOR) and hypoxia (Hx) (
∼ 39 mmHg; at black bar) in CSE +/+ and CSE−/− mice. Integrated carotid body sensory activity (CB activity) is presented as impulses per second (imp/s). Superimposed action potentials from the single fiber are presented in Inset. (C) Carotid body responses to graded hypoxia from CSE+/+ and CSE−/− mice, measured as the difference in response between baseline and hypoxia (Δimp/s). Data are mean ± SEM of n = 24 (CSE+/+) and n = 23 (CSE−/−) fibers from eight mice each. (D) H2S levels (mean ± SEM) in carotid bodies from CSE+/+ and CSE−/− mice under normoxia (NOR) and hypoxia (Hx) ( ∼ 40 mmHg) from four independent experiments. (E) Example illustrating carotid body responses to CO2
∼ 40 mmHg) from four independent experiments. (E) Example illustrating carotid body responses to CO2  in CSE+/+ and CSE−/− mice. (F) Average data (mean ± SEM) of CO2 response from n = 24 (CSE +/+) and n = 19 (CSE−/−) fibers from eight mice in each group. *** and **, P < 0.001 and P < 0.01, respectively; n.s. (not significant), P > 0.05.
in CSE+/+ and CSE−/− mice. (F) Average data (mean ± SEM) of CO2 response from n = 24 (CSE +/+) and n = 19 (CSE−/−) fibers from eight mice in each group. *** and **, P < 0.001 and P < 0.01, respectively; n.s. (not significant), P > 0.05.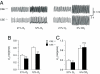
 = 38 mmHg; at black bar) in vehicle- and PAG-treated rats (Left). Average (mean ± SEM) data of sensory response to graded hypoxia (Right), PAG− n = 12 fibers from six rats; PAG+ n = 10 fibers from six rats. (C) Example of carotid body response to CO2 in the same rats as in B (
= 38 mmHg; at black bar) in vehicle- and PAG-treated rats (Left). Average (mean ± SEM) data of sensory response to graded hypoxia (Right), PAG− n = 12 fibers from six rats; PAG+ n = 10 fibers from six rats. (C) Example of carotid body response to CO2 in the same rats as in B ( ∼ 68 mmHg; at black bar (Left)] and average (mean ± SEM) data of CO2 response (Right). Data derived from n = 9 fibers (PAG−) and n = 10 (PAG+) fibers from six rats each. In B and C, integrated carotid body sensory activity (CB activity) is presented as impulses per second (imp/s). Superimposed action potentials from the single fiber are presented in Inset. **, P < 0.01.
∼ 68 mmHg; at black bar (Left)] and average (mean ± SEM) data of CO2 response (Right). Data derived from n = 9 fibers (PAG−) and n = 10 (PAG+) fibers from six rats each. In B and C, integrated carotid body sensory activity (CB activity) is presented as impulses per second (imp/s). Superimposed action potentials from the single fiber are presented in Inset. **, P < 0.01.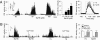
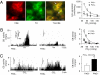
 = 42 mmHg (Right)]. Data in middle and right panels were obtained from n = 13 fibers from six rats. (B) Effect of Ca2+ free medium on rat carotid body responses to 100 μM NaHS and hypoxia (Hx) (
= 42 mmHg (Right)]. Data in middle and right panels were obtained from n = 13 fibers from six rats. (B) Effect of Ca2+ free medium on rat carotid body responses to 100 μM NaHS and hypoxia (Hx) ( = 42 mmHg; at black bar). CaCl2 was replaced by 3 mM MgCl2 and 5 mM EGTA was added to the medium. (Left) Example and Right average (mean ± SEM) data from five rats (n = 8 fibers). In A and B, Integrated carotid body sensory activity (CB activity) is presented as impulses per second (imp/s). Superimposed action potentials from the single fiber are presented in the inset. **, P < 0.01; n.s. (not significant), P > 0.05.
= 42 mmHg; at black bar). CaCl2 was replaced by 3 mM MgCl2 and 5 mM EGTA was added to the medium. (Left) Example and Right average (mean ± SEM) data from five rats (n = 8 fibers). In A and B, Integrated carotid body sensory activity (CB activity) is presented as impulses per second (imp/s). Superimposed action potentials from the single fiber are presented in the inset. **, P < 0.01; n.s. (not significant), P > 0.05.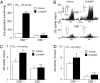
 ∼ 146 mmHg) from CSE+/+ and CSE−/− mice. Data presented are mean ± SEM from three experiments. Examples of baseline and hypoxic response (Hx) (
∼ 146 mmHg) from CSE+/+ and CSE−/− mice. Data presented are mean ± SEM from three experiments. Examples of baseline and hypoxic response (Hx) ( ∼ 40 mmHg; at black bar) of carotid bodies from vehicle- and Cr(III)MP-treated CSE+/+ and CSE−/− mice (B) and average data (mean ± SEM) from six mice in each group (n = 8–12 fibers) in C and D. In B, Integrated carotid body sensory activity (CB activity) is presented as impulses per second (imp/s). Superimposed action potentials from the single fiber are presented in Inset. *** and *, P < 0.001 and P < 0.05, respectively; n.s. (not significant), P > 0.05.
∼ 40 mmHg; at black bar) of carotid bodies from vehicle- and Cr(III)MP-treated CSE+/+ and CSE−/− mice (B) and average data (mean ± SEM) from six mice in each group (n = 8–12 fibers) in C and D. In B, Integrated carotid body sensory activity (CB activity) is presented as impulses per second (imp/s). Superimposed action potentials from the single fiber are presented in Inset. *** and *, P < 0.001 and P < 0.05, respectively; n.s. (not significant), P > 0.05.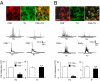
 = 36 mmHg) or high K+ (40 mM). Black bar represents the duration of hypoxia or K+ application. (Bottom) Average data (mean ± SEM) of total catecholamine (CA) secreted during Hx or K+ (CA molecules 107 i.e., number of secretory events multiplied by catecholamine molecules secreted per event). n = 9 cells each from CSE+/+ and CSE−/− and n = 10–12 cells from rat pups. **, P < 0.01; n.s. (not significant), P > 0.05 compared with CSE+/+ mice or vehicle-treated rat cells.
= 36 mmHg) or high K+ (40 mM). Black bar represents the duration of hypoxia or K+ application. (Bottom) Average data (mean ± SEM) of total catecholamine (CA) secreted during Hx or K+ (CA molecules 107 i.e., number of secretory events multiplied by catecholamine molecules secreted per event). n = 9 cells each from CSE+/+ and CSE−/− and n = 10–12 cells from rat pups. **, P < 0.01; n.s. (not significant), P > 0.05 compared with CSE+/+ mice or vehicle-treated rat cells.Comment in
-
H2S and O2 sensing.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Sep 14;107(37):E141; author reply E142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1009210107. Epub 2010 Aug 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20807752 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Hydrogen sulfide (H(2)S): a physiologic mediator of carotid body response to hypoxia.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;758:109-13. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-4584-1_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 23080150 Review.
-
Gaseous transmitter regulation of hypoxia-evoked catecholamine secretion from murine adrenal chromaffin cells.J Neurophysiol. 2021 May 1;125(5):1533-1542. doi: 10.1152/jn.00669.2020. Epub 2021 Mar 17. J Neurophysiol. 2021. PMID: 33729866 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous H2S is required for hypoxic sensing by carotid body glomus cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012 Nov 1;303(9):C916-23. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00100.2012. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22744006 Free PMC article.
-
CaV3.2 T-type Ca²⁺ channels in H₂S-mediated hypoxic response of the carotid body.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015 Jan 15;308(2):C146-54. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00141.2014. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25377087 Free PMC article.
-
Gaseous messengers in oxygen sensing.J Mol Med (Berl). 2012 Mar;90(3):265-72. doi: 10.1007/s00109-012-0876-1. Epub 2012 Feb 16. J Mol Med (Berl). 2012. PMID: 22349394 Review.
Cited by
-
"Oxygen Sensing" by Na,K-ATPase: These Miraculous Thiols.Front Physiol. 2016 Aug 2;7:314. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00314. eCollection 2016. Front Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27531981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Seeking Illumination: The Path to Chemiluminescent 1,2-Dioxetanes for Quantitative Measurements and In Vivo Imaging.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Jul 6;54(13):2844-2857. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00185. Epub 2021 Jun 10. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 34110136 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen sulfide and hypoxia-induced changes in TASK (K2P3/9) activity and intracellular Ca(2+) concentration in rat carotid body glomus cells.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2015 Aug 15;215:30-8. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2015.04.012. Epub 2015 May 5. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25956223 Free PMC article.
-
Depolarizing actions of hydrogen sulfide on hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus neurons.PLoS One. 2013 May 17;8(5):e64495. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064495. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23691233 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-trappable fluorescent probes for endogenous hydrogen sulfide signaling and imaging H2O2-dependent H2S production.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Apr 30;110(18):7131-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1302193110. Epub 2013 Apr 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23589874 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Prabhakar NR. Oxygen sensing by the carotid body chemoreceptors. J Appl Physiol. 2000;88:2287–2295. - PubMed
-
- Prabhakar NR, Kumar GK, Chang CH, Agani FH, Haxhiu MA. Nitric oxide in the sensory function of the carotid body. Brain Res. 1993;625:16–22. - PubMed
-
- Williams SE, et al. Hemoxygenase-2 is an oxygen sensor for a calcium-sensitive potassium channel. Science. 2004;306:2093–2097. - PubMed
-
- Prabhakar NR. NO and CO as second messengers in oxygen sensing in the carotid body. Respir Physiol. 1999;115:161–168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

