A novel function of microRNA let-7d in regulation of galectin-3 expression in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder rat brain
- PMID: 20557304
- PMCID: PMC8094722
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2010.00410.x
A novel function of microRNA let-7d in regulation of galectin-3 expression in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder rat brain
Abstract
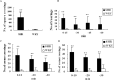
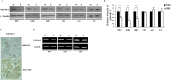
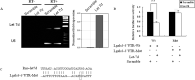
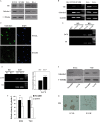
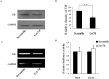
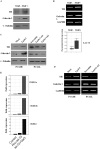
In this study we investigated the locomotor activity and non-selective attention in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) with control Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) rats, which were employed as an attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) model. In open-field test and làt maze, SHR rats were found to be much more spontaneously active than WKY rats. As compared with WKY rats, a lower level of galectin-3 was observed in SHR brain prefrontal cortex (PFC), which was the major affected brain area of ADHD. Through miRNA microarray screening, rno-let-7d was noted to be solely upregulated in SHR PFC. Interestingly, rno-let-7d had a binding site at galectin-3 mRNA and was shown to regulate galectin-3 3' untranslated region (UTR) directly. Mutation of galectin-3 3'UTR by one nucleotide of the seed sequence prevented rno-let-7d regulation of the 3' UTR completely. Although rno-let-7d did not directly regulate tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) 3'UTR, the level of galectin-3 was important for cAMP response element binding protein, the major transcript factor for TH gene. Either overexpression or downexpression of galectin-3 could result in modulation of TH expression in both PC12H and PC12L cells. In conclusion, our data suggested a novel function of rno-let-7d in regulation of galectin-3 and in ADHD development. Rno-let-7d, which is increased in the PFC of SHR brain, negatively regulated galectin-3, which is coupled with TH expression regulation.
© 2010 The Authors; Brain Pathology © 2010 International Society of Neuropathology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Circulating MicroRNA Let-7d in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder.Neuromolecular Med. 2015 Jun;17(2):137-46. doi: 10.1007/s12017-015-8345-y. Epub 2015 Feb 28. Neuromolecular Med. 2015. PMID: 25724585
-
Theobromine improves hyperactivity, inattention, and working memory via modulation of dopaminergic neural function in the frontal cortex of spontaneously hypertensive rats.Food Funct. 2024 May 20;15(10):5579-5595. doi: 10.1039/d4fo00683f. Food Funct. 2024. PMID: 38713055
-
Transcriptional profiling of SHR/NCrl prefrontal cortex shows hyperactivity-associated genes responsive to amphetamine challenge.Genes Brain Behav. 2017 Sep;16(7):664-674. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12388. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Genes Brain Behav. 2017. PMID: 28422445
-
Hypodopaminergic and hypernoradrenergic activity in prefrontal cortex slices of an animal model for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder--the spontaneously hypertensive rat.Behav Brain Res. 2002 Mar 10;130(1-2):191-6. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(01)00425-9. Behav Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 11864734 Review.
-
[Advances in the Pathophysiology and Drug Discovery of Novel Therapeutics for Attention-Deficit/hyperactivity Disorder].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2024;144(12):1039-1044. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.24-00126. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2024. PMID: 39617465 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Modulation of BK channel by MicroRNA-9 in neurons after exposure to HIV and methamphetamine.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013 Dec;8(5):1210-23. doi: 10.1007/s11481-013-9446-8. Epub 2013 Mar 19. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23508624 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs: a light into the "black box" of neuropediatric diseases?Neuromolecular Med. 2012 Dec;14(4):244-61. doi: 10.1007/s12017-012-8193-y. Epub 2012 Jul 19. Neuromolecular Med. 2012. PMID: 22810393
-
MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers for diagnosis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Mar;19(3):557-562. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.380880. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 37721284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-19a regulates PTEN expression to mediate glycogen synthesis in hepatocytes.Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 26;5:11602. doi: 10.1038/srep11602. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26111969 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Action of Fluoxetine is Associated with a Reduction in Prefrontal Cortical miR-1971 Expression Levels in a Mouse Model of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder.Front Psychiatry. 2013 Jul 10;4:66. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2013.00066. eCollection 2013. Front Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23847554 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Aspide R, Fresiello A, De Filippis G, Gironi Carnevale UA, Sadile AG (2000) Non‐selective attention in a rat model of hyperactivity and attention deficit: subchronic methylphenydate and nitric oxide synthesis inhibitor treatment. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24:59–71. - PubMed
-
- Bellac CL, Coimbra RS, Simon F, Imboden H, Leib SL (2007) Gene and protein expression of galectin‐3 and galectin‐9 in experimental pneumococcal meningitis. Neurobiol Dis 28:175–183. - PubMed
-
- Brown RT, Freeman WS, Perrin JM, Stein MT, Amler RW, Feldman HM et al (2001) Prevalence and assessment of attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder in primary care settings. Pediatrics 107:E43. - PubMed
-
- Bushati N, Cohen SM (2008) MicroRNAs in neurodegeneration. Curr Opin Neurobiol 18:292–296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

