Mast cells and MMP-9 in the lamina propria during eruption of rat molars: quantitative and immunohistochemical evaluation
- PMID: 20557403
- PMCID: PMC2913021
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2010.01249.x
Mast cells and MMP-9 in the lamina propria during eruption of rat molars: quantitative and immunohistochemical evaluation
Abstract
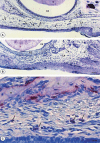
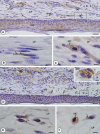
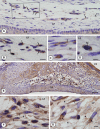
During the active tooth eruption process, structural changes in the lamina propria are necessary to provide extracellular matrix remodelling and for the establishment of the eruptive pathway. A large number of resident cells, recruited cells and proteases have been demonstrated in the eruptive process, but the participation of MMP-9 and mast cells has not yet been demonstrated. In this study, we set out to evaluate the intensity of MMP-9 immunoexpression, the frequency of mast cells and the correlation between the incidence of mast cells and bone resorption in different phases of tooth eruption. Fragments of maxilla containing first molars, obtained from 9-, 11-, 13- and 16-day-old rats, were fixed in 4% formaldehyde, decalcified and embedded in paraffin. Sagittal sections were stained with Masson's trichrome or submitted to the tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase method for quantification of osteoclasts. Sections stained by 1% toluidine blue were used for quantification of metachromatic mast cells mm(-2) of lamina propria. The expression of MMP-9 in the lamina propria was evaluated by immunohistochemistry. In the 9-day-old rats, the lamina propria contained few mast cells and occasional osteoclasts were found in the bone surface overlying the occlusal portion of the tooth germs. Otherwise, a significant increase in the number of mast cells was observed in the intra-osseous phase of tooth eruption (11-day-old rats), period in which numerous TRAP-positive osteoclasts were found in the bone surface. MMP-9 immunolabelling was detected in fibroblasts, mast cells and macrophage-like cells of the lamina propria in all ages studied. However, an enhanced immunolabelling was evident in the advanced phase of tooth eruption (16-day-old rats). During the intra-osseous phase, the parallel between the high frequency of both mast cells and osteoclasts suggests that mast cells could exert a paracrine function on the osteoclasts and then stimulate bone resorption. The immunoexpression of MMP-9 in different cells of lamina propria, including mast cells, indicates that this enzyme participates in the degradation of ECM, mainly during late phase of mucosal penetration. Thus mast cells and MMP-9 are involved in the complex process of degradation of the eruptive pathway extracellular matrix.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 and Acid Phosphatase in the Degradation of the Lamina Propria of Eruptive Pathway of Rat Molars.Cells. 2018 Nov 10;7(11):206. doi: 10.3390/cells7110206. Cells. 2018. PMID: 30423799 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis and reduced microvascular density of the lamina propria during tooth eruption in rats.J Anat. 2015 Oct;227(4):487-96. doi: 10.1111/joa.12359. Epub 2015 Jul 30. J Anat. 2015. PMID: 26228092 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse effects of c-src deficiency on molar tooth development and eruption in mice.Arch Histol Cytol. 2007 Apr;70(1):63-78. doi: 10.1679/aohc.70.63. Arch Histol Cytol. 2007. PMID: 17558145
-
Reduced growth hormone receptor immunoreactivity in osteoclasts adjacent to the erupting molar in the incisor-absent (osteopetrotic) rat.Eur J Oral Sci. 2003 Dec;111(6):503-9. doi: 10.1111/j.0909-8836.2003.00075.x. Eur J Oral Sci. 2003. PMID: 14632687
-
Mechanism of human tooth eruption: review article including a new theory for future studies on the eruption process.Scientifica (Cairo). 2014;2014:341905. doi: 10.1155/2014/341905. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Scientifica (Cairo). 2014. PMID: 24688798 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural and functional changes in the alveolar bone osteoclasts of estrogen-treated rats.J Anat. 2012 Jan;220(1):77-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2011.01449.x. Epub 2011 Nov 16. J Anat. 2012. PMID: 22092353 Free PMC article.
-
Additional Insights Into the Role of Osteocalcin in Osteoblast Differentiation and in the Early Steps of Developing Alveolar Process of Rat Molars.J Histochem Cytochem. 2023 Dec;71(12):689-708. doi: 10.1369/00221554231211630. Epub 2023 Nov 12. J Histochem Cytochem. 2023. PMID: 37953508 Free PMC article.
-
Gross morphological features of the organ surface primo-vascular system revealed by hemacolor staining.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:350815. doi: 10.1155/2013/350815. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23986781 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric oxide-mediated vasodilation increases blood flow during the early stages of stress fracture healing.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2014 Feb 15;116(4):416-24. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00957.2013. Epub 2013 Dec 19. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2014. PMID: 24356518 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Er,Cr:YSGG laser application in the treatment of experimental periodontitis.Lasers Med Sci. 2015 Apr;30(3):993-9. doi: 10.1007/s10103-014-1526-3. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Lasers Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 24477391
References
-
- Artuc M, Steckelings UM, Henz BM. Mast cell–fibroblast interactions: human mast cells as source and inducers of fibroblast and epithelial growth factors. J Invest Dermatol. 2002;118:391–395. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett JD, Zhou Z, Skobe Z, et al. Delayed tooth eruption in membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase deficient mice. Connect Tissue Res. 2003;44:300–304. - PubMed
-
- Beertsen W, Holmbeck K, Niehof A, et al. On the role of MT1-MMP, a matrix metalloproteinase essential to collagen remodeling, in murine molar eruption and root growth. Eur J Oral Sci. 2002;110:445–451. - PubMed
-
- Birkedal-Hansen H, Moore WGI, Bodden MK, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases: a review. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1993;4:197–250. - PubMed
-
- Blavier L, Delaissé JM. Matrix metalloproteinases are obligatory for the migration of preosteoclasts to the developing marrow cavity of primitive long bones. J Cell Sci. 1995;108:3649–3659. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

