Role of serotonin in central dopamine dysfunction
- PMID: 20557570
- PMCID: PMC6493878
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2010.00135.x
Role of serotonin in central dopamine dysfunction
Abstract
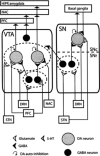
The interaction between serotonin (5-HT) and dopamine (DA)-containing neurons in the brain is a research topic that has raised the interest of many scientists working in the field of neuroscience since the first demonstration of the presence of monoamine-containing neurons in the mid 1960. The bulk of neuroanatomical data available clearly indicate that DA-containing neurons in the brain receive a prominent innervation from serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) originating in the raphe nuclei of the brainstem. Compelling electrophysiological and neurochemical data show that 5-HT can exert complex effects on the activity of midbrain DA neurons mediated by its various receptor subtypes. The main control seems to be inhibitory, this effect being more marked in the mesocorticolimbic DA system as compared to the DA nigrostriatal system. In spite of a direct effect of 5-HT by its receptors located on DA cells, 5-HT can modulate their activity indirectly, modifying gamma-aminobutyric (GABA)-ergic and glutamatergic input to the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc). Although 5-HT/DA interaction in the brain has been extensively studied, much work remains to be done to clarify this issue. The recent development of subtype-selective ligands for 5-HT receptors will not only allow a detailed understanding of this interaction but also will lead to the development of new treatment strategies, appropriate for those neuropsychiatric disorders in which an alteration of the 5-HT/DA balance is supposed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Dahlström A, Fuxe K. Evidence for the existence of monoamine‐containing neurons in the central nervous system. Part I. Demonstration of monoamines in the cell bodies of brain stem neurons. Acta Physiol Scand 1964;62:1–55. - PubMed
-
- Bannon MJ, Roth RH. Pharmacology of mesocortical dopamine neurons. Pharmacol Rev 1983;35:53–68. - PubMed
-
- Roth RH, Wolf ME, Deutch AY. Neurochemistry of midbrain dopamine systems In: Meltzer HY, editor. Psychopharmacology: The third generation of progress. New York : Raven Press, 1987;81–94.
-
- Kalivas PW. Neurotransmitter regulation of dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area. Brain Res Rev 1993;18:75–113. - PubMed
-
- White FJ. Synaptic regulation of mesocorticolimbic dopamine neurons. Annu Rev Neurosci 1996;19:405–436. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

